- English
- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
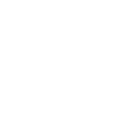
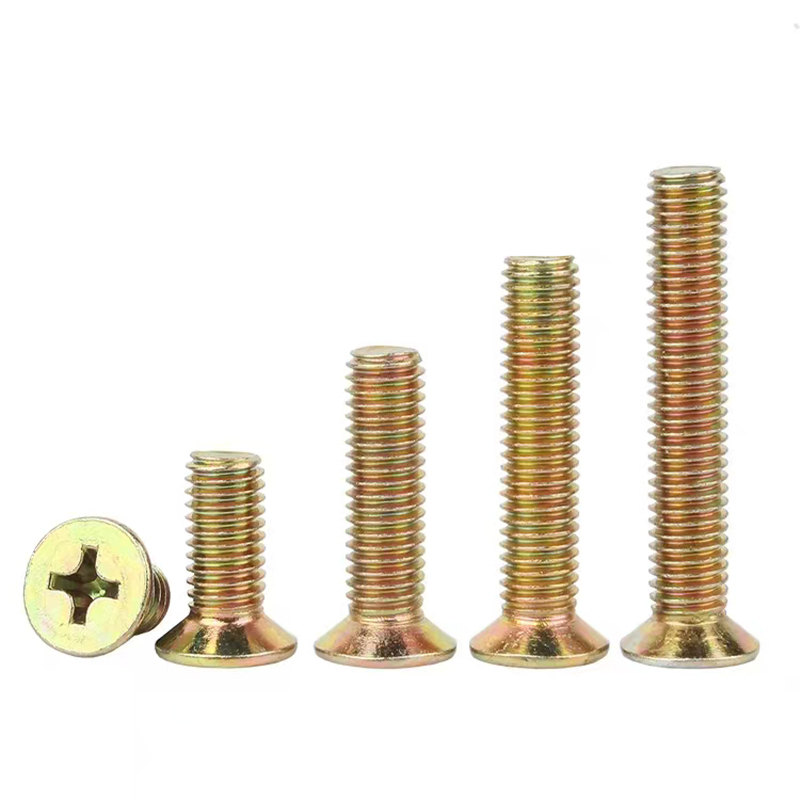
How sustainable are hot-dip galvanized chemical bolts?
2026-01-06
Hot-dip galvanized chemical bolts are a staple in the construction industry, known for their enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion. However, the conversation around their sustainability often leaves room for debate. While they promise longevity, is the process itself environmentally friendly, and how do these factors balance against each other?
Understanding Hot-Dip Galvanization
Hot-dip galvanization involves coating steel bolts in molten zinc to protect against corrosion. This method has proven effective, especially in environments prone to harsh weather. By creating a robust barrier, the bolts endure longer, reducing the frequency of replacements. This is a positive sign for resource conservation.
Yet, the process requires significant energy and material input. The production involves heating zinc and maintaining it in a molten state, which could raise concerns about energy consumption. Some colleagues have found that modern facilities, like those at Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd., use more efficient systems, but it’s not a universal standard.
There’s also the question of zinc supply and its future sustainability. Although zinc is abundantly available, its extraction and processing come with an environmental cost. Balancing these factors can be tricky when considering the long-term impact on the environment.
Application and Longevity
One of the strongest arguments for using hot-dip galvanized chemical bolts is their impressive lifespan. In my experience, these bolts easily outperform their non-galvanized counterparts in corrosive settings such as near coastlines or in industrial applications where chemical exposure is constant. The longevity reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Replacing bolts may seem trivial, but consider the labor, energy, and additional materials involved. There’s a clear environmental benefit to needing fewer replacements over large infrastructures. The extended life effectively plays into the sustainability equation by offsetting the initial environmental cost of production.
For example, in a project we did near a coastal industrial site, switching to these bolts increased the structure’s maintenance intervals, saving costs and resources in the long run. This showcases how initial investments in quality materials can bear sustainable outcomes over time.
Challenges in Waste Management
The end-of-life stage of these products is another matter worth understanding. Galvanized steel can indeed be recycled, which contributes to its sustainability appeal. However, separating the zinc coating in the recycling process can be a hurdle. In practice, not all recycling facilities are equipped to handle this efficiently.
I’ve worked on projects where we focused on ensuring that used bolts were directed to specialized recycling programs. Fortunately, some areas have seen advancements, where the emerging technologies allow for easier separation and recycling, making galvanized products more appealing under a sustainability lens.
But there’s always room for improvement. Enhancements in end-of-life processing could significantly impact how these bolts are perceived in terms of environmental responsibility.
Environmental Regulations and Compliance
From a regulatory perspective, galvanizing processes must meet environmental standards, which can vary widely depending on the region. Companies like Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. comply with these regulations, reflecting an adherence to maintaining environmental balance.
It is crucial to work with suppliers who not only comply with these regulations but also proactively seek ways to minimize their environmental footprint. Innovations in production technology play a vital part here.
Thankfully, ongoing research in improving galvanizing techniques continues to make the process more eco-friendly, which gradually mitigates some of the energy and resource concerns initially present.
Refleksyon final
Ultimately, the sustainability of hot-dip galvanized chemical bolts hinges on more than just the end product’s durability. It encompasses the production process, life cycle, recyclability, and the compliance of manufacturers with environmental regulations.
In the case of Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd., being situated in a hub of standard part production allows access to efficient logistics and production practices, theoretically reducing the overall carbon footprint. Leveraging these advantages is crucial for the future of sustainable construction materials.
While current methods show promising aspects of sustainability, ongoing innovation and commitment to environmental responsibility remain key to ensuring that hot-dip galvanized bolts meet the long-term sustainability goals of the industry.