- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
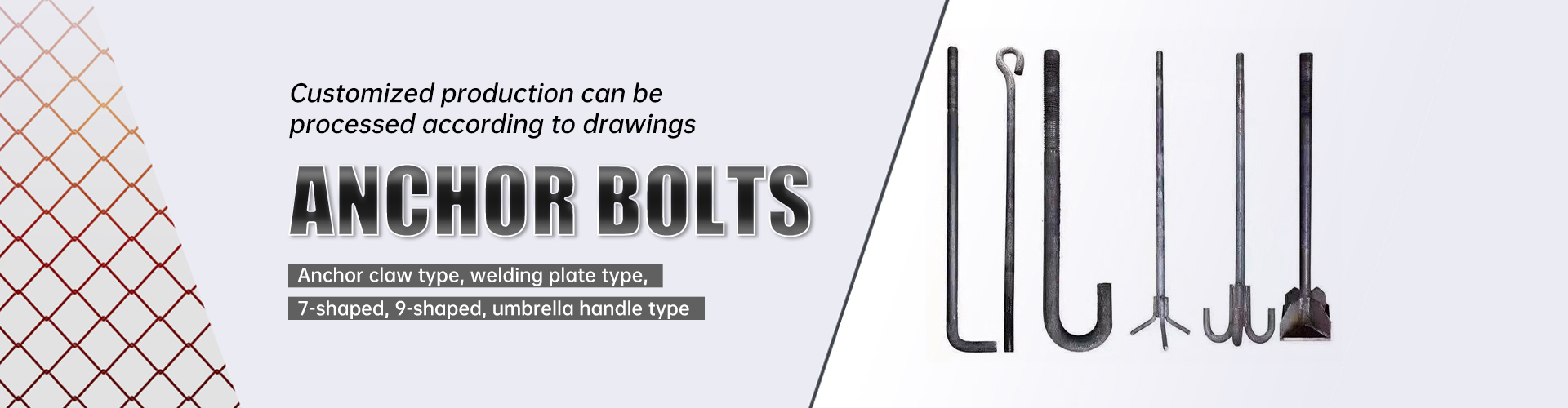
Products
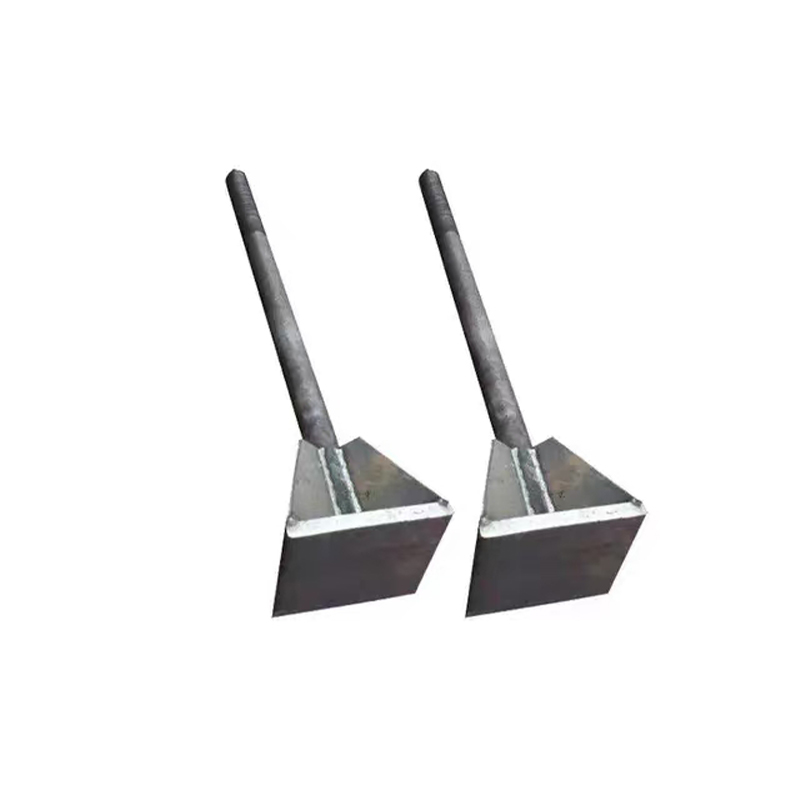
Hot-dip galvanized embedded plate
Same as electrogalvanized embedded plate, using Q235 or Q355 carbon steel, steel plate thickness 8-50mm, anchor bar diameter 10-32mm, in line with GB/T 700 standard.
Description
marker
Material and process
Base material: Same as electrogalvanized embedded plate, using Q235 or Q355 carbon steel, steel plate thickness 8-50mm, anchor bar diameter 10-32mm, in line with GB/T 700 standard.
Surface treatment: Immersed in molten zinc liquid to form a 45-85μm coating, in line with GB/T 13912-2022 standard, salt spray test can reach more than 300 hours without red rust, suitable for harsh environments.
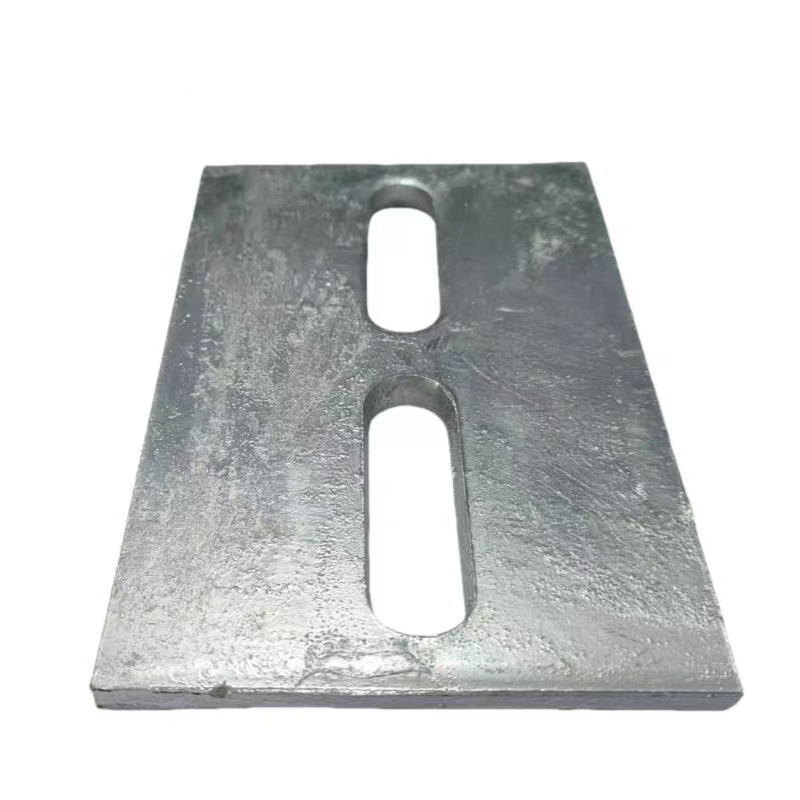

Structural design
Anchor bar form: Straight anchor bars are mostly used, and the anchor plate thickness is ≥0.6 times the anchor bar diameter (for example, when the anchor bar diameter is 20mm, the anchor plate thickness is ≥12mm) to ensure shear and tensile performance.
Special design: Some products are equipped with shear key components (such as L-shaped angle irons), which can increase the horizontal shear capacity by more than 30%, suitable for heavy-load scenarios such as bridge bearings.
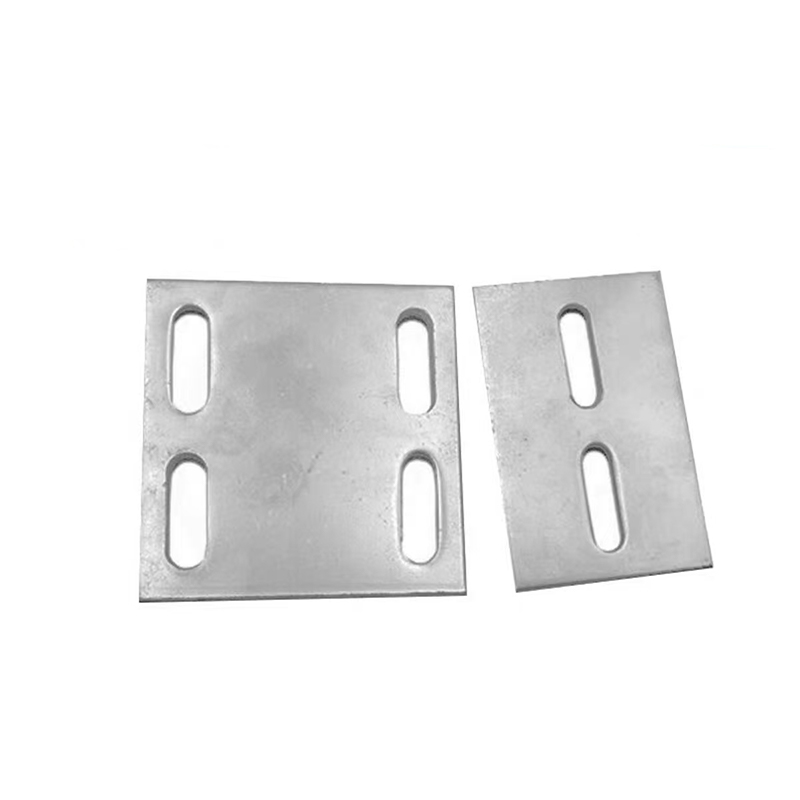

Performance characteristics
Anti-corrosion performance: The coating thickness is 3-7 times that of electrogalvanizing, and the corrosion resistance is significantly improved. It is suitable for outdoor, marine, chemical and other environments.
Bearing capacity: Taking M16 anchor bars as an example, the tensile bearing capacity in C40 concrete is about 55kN, and the shear bearing capacity is about 28kN, which is suitable for high-load projects.
Economic efficiency: Although the initial cost is high, the service life can reach more than 20 years, and the comprehensive cost is lower than electrogalvanizing.
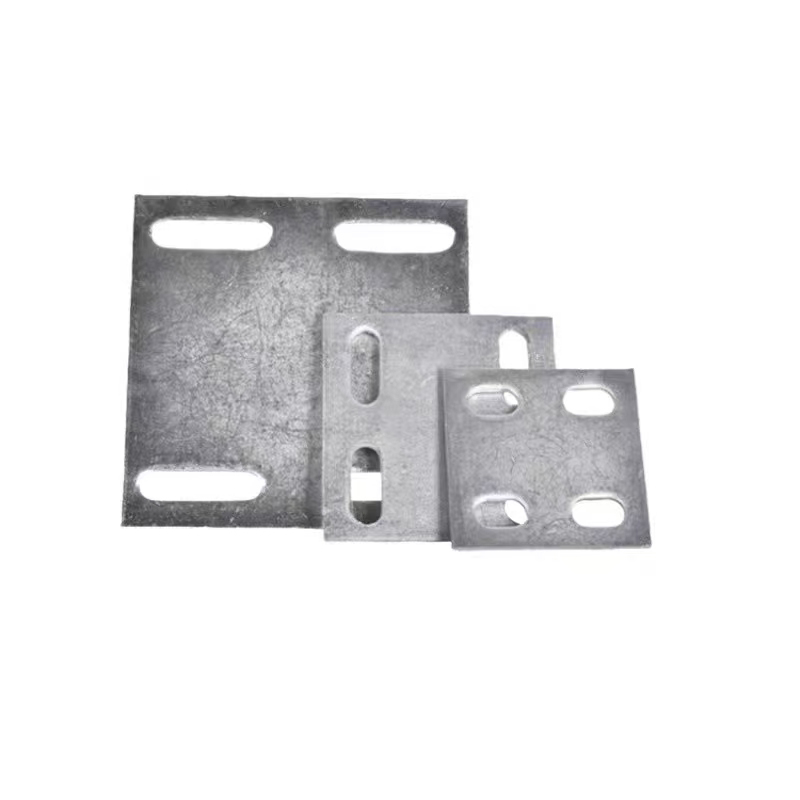

Application scenarios
Infrastructure: bridges, ports, power towers, highway sound barriers, etc.
Industrial buildings: photovoltaic brackets, heavy machinery foundations, and mining equipment fixation.

Key comparison and selection suggestions
| Comparison items | Electrogalvanized embedded plate | Hot-dip galvanized embedded plate |
| Coating thickness | 5-12μm | 45-85μm |
| Salt spray test | 24-48 hours (neutral salt spray) | More than 300 hours (neutral salt spray) |
| Corrosion resistance | Indoor or slightly humid environment | Outdoor, high humidity, industrial pollution environment |
| Bearing capacity | Medium (lower design value) | High (higher design value) |
| Environmental protection | No hexavalent chromium, excellent environmental protection | May contain hexavalent chromium, must comply with RoHS standards |
| Cost | Low (low initial investment) | High (high initial investment, low long-term cost) |

Selection suggestions:
Environmental factors: Hot-dip galvanizing is preferred for outdoor or highly corrosive environments; electrogalvanizing can be selected for indoor or dry environments.
Load requirements: Hot-dip galvanizing must be used in high-load scenarios (such as bridges and heavy machinery), and weld flaw detection and pull-out tests must be performed in accordance with GB 50205-2020.
Environmental requirements: Electrogalvanizing is recommended for sensitive industries such as medical and food; hot-dip galvanizing is acceptable for general industrial projects (it is necessary to confirm that the hexavalent chromium content is ≤1000ppm).
Installation Note: After welding, the damaged coating needs to be repaired with zinc (such as coating with zinc-rich paint) to ensure the overall anti-corrosion performance.