- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
Products
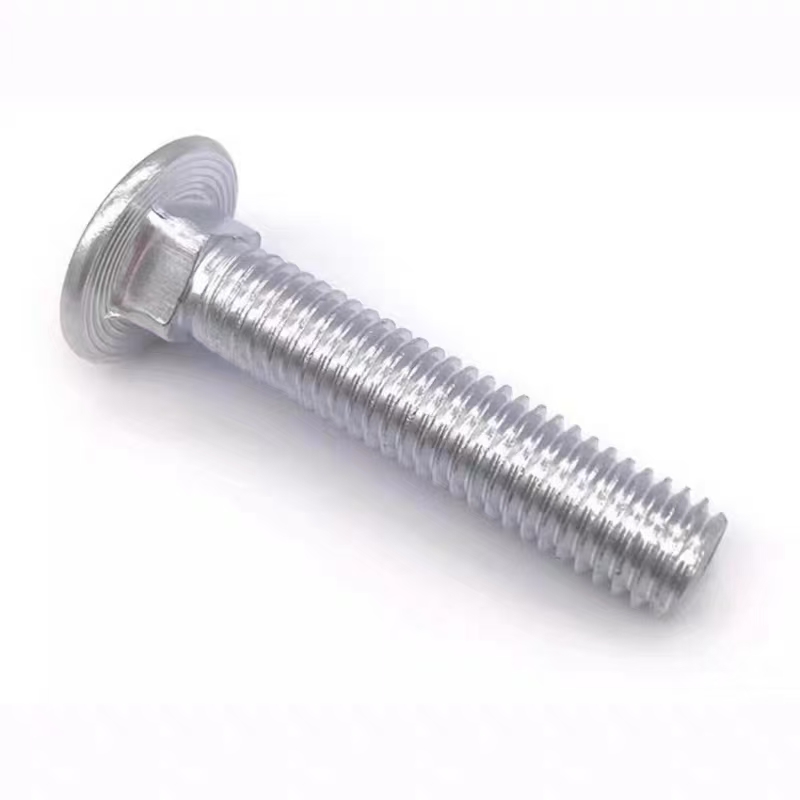
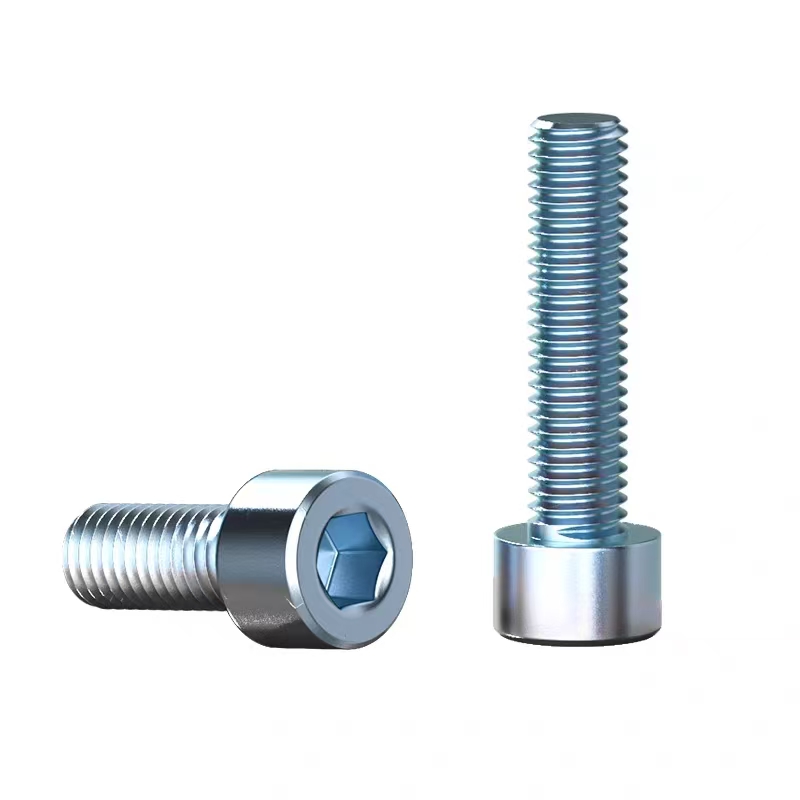
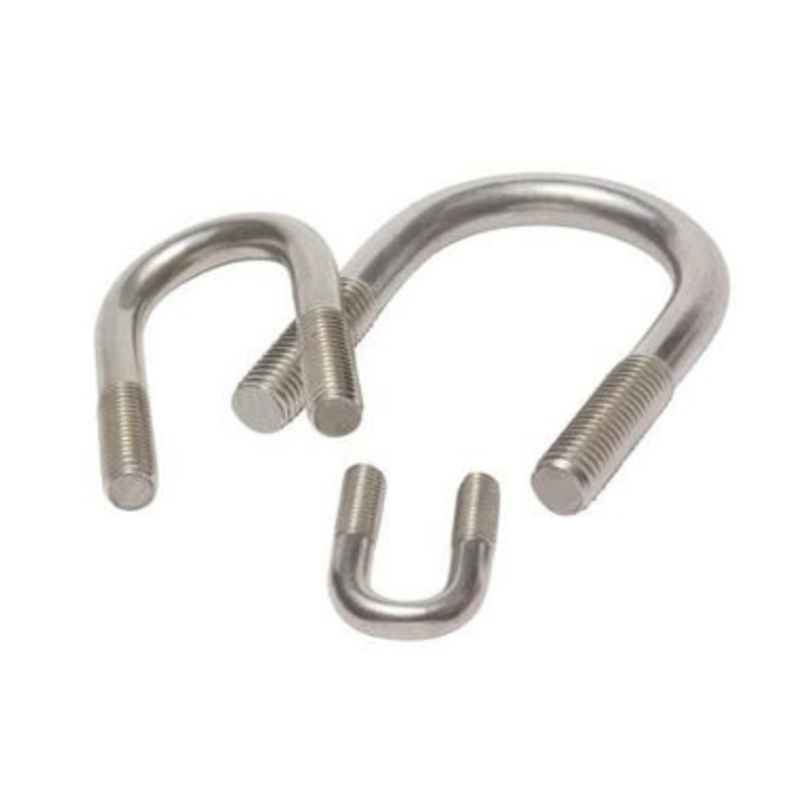
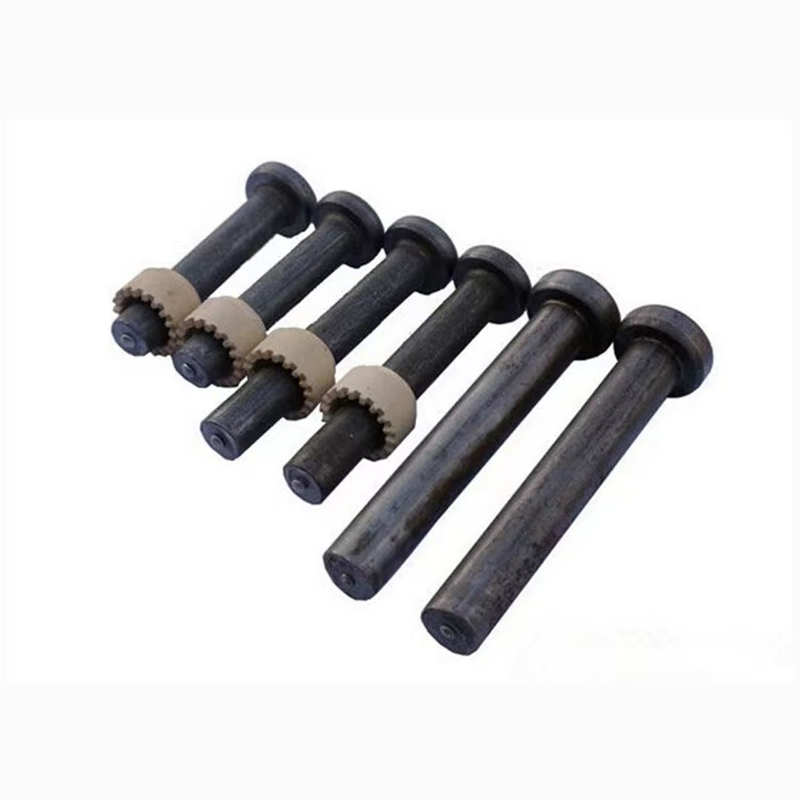
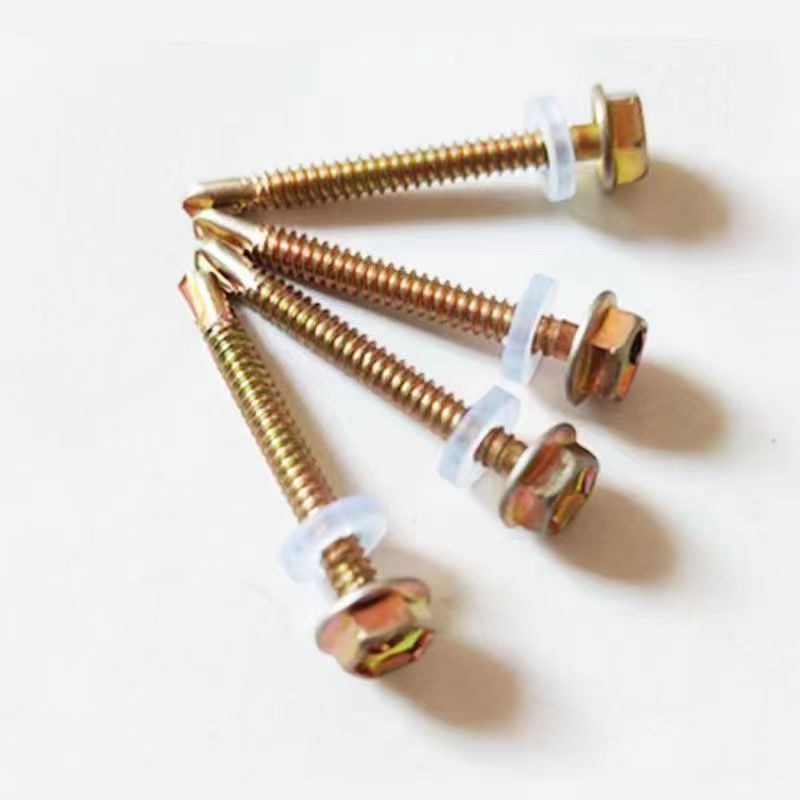
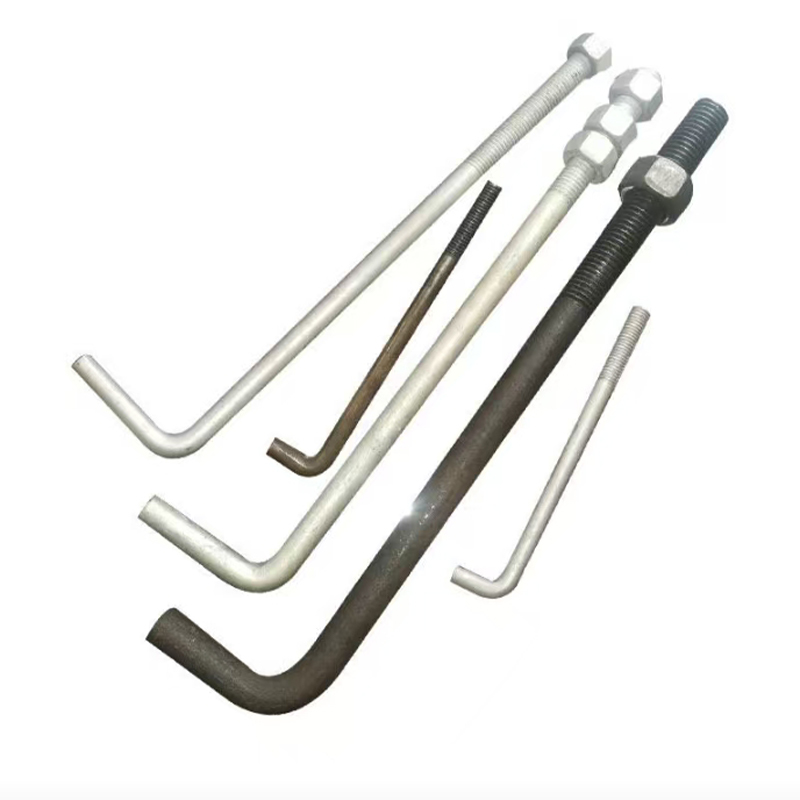
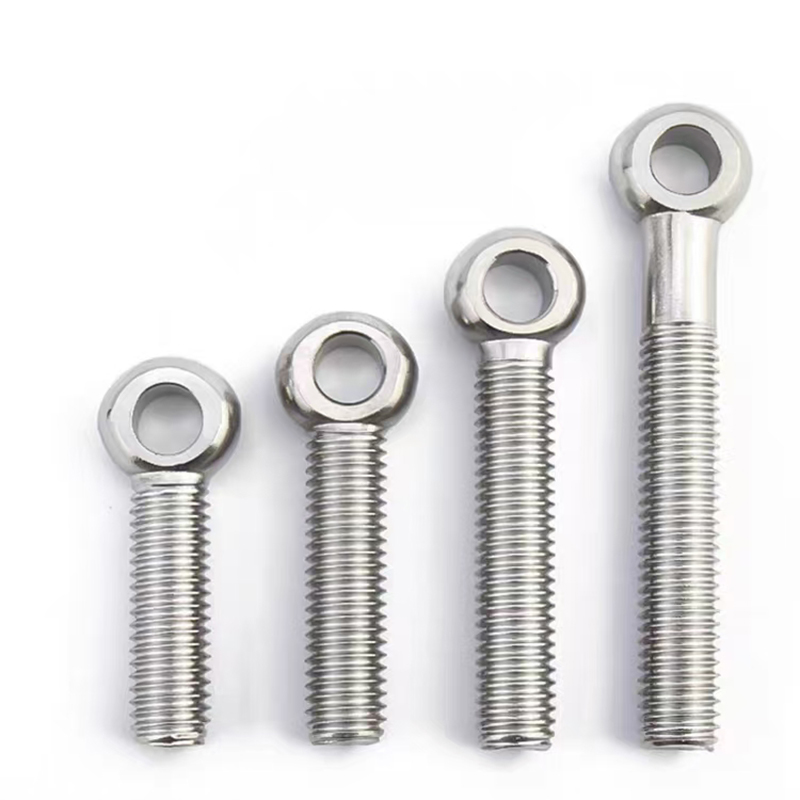
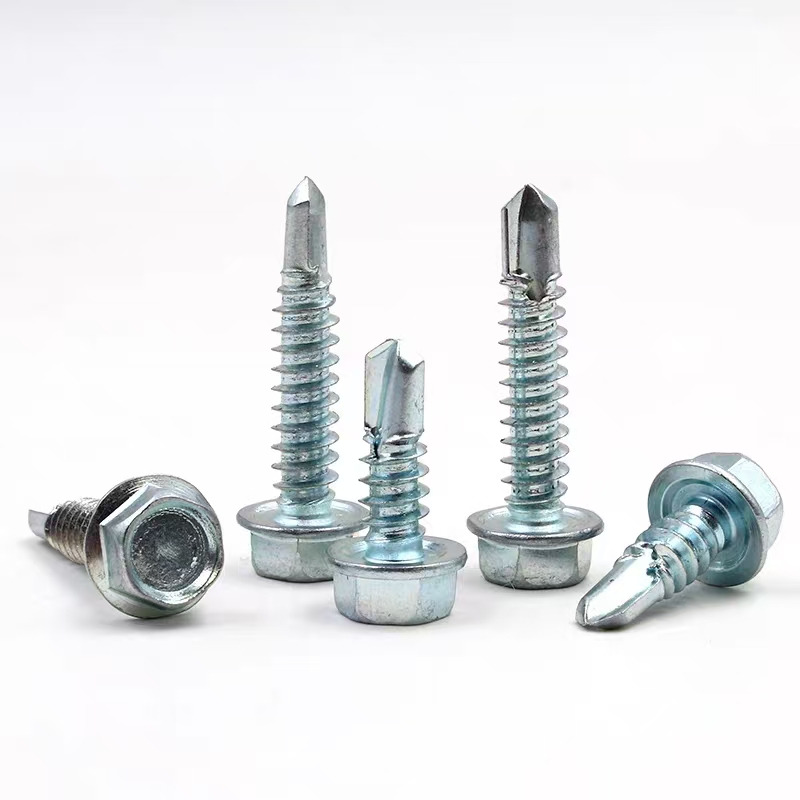
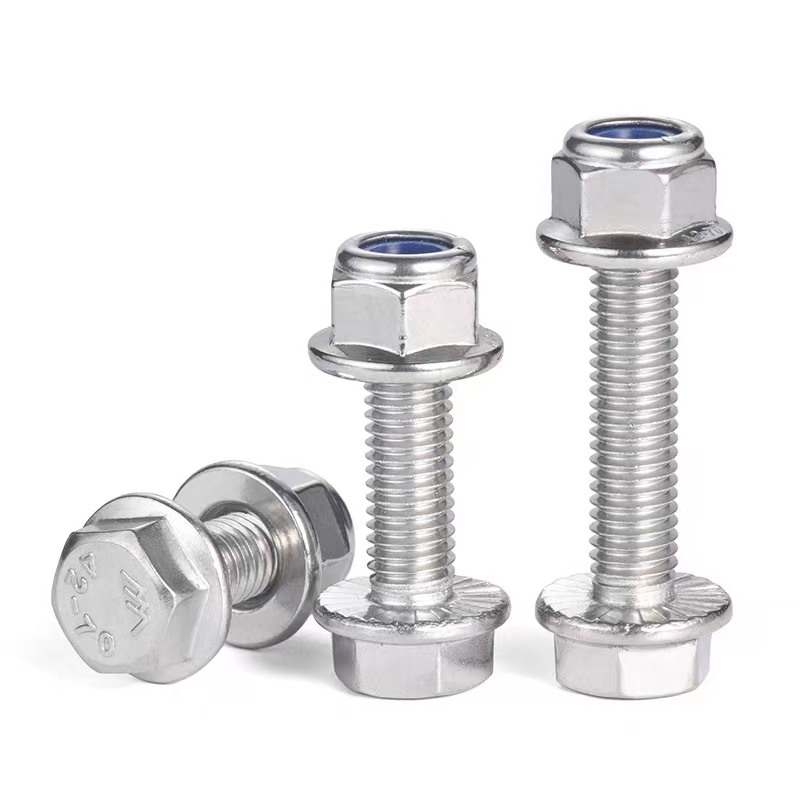
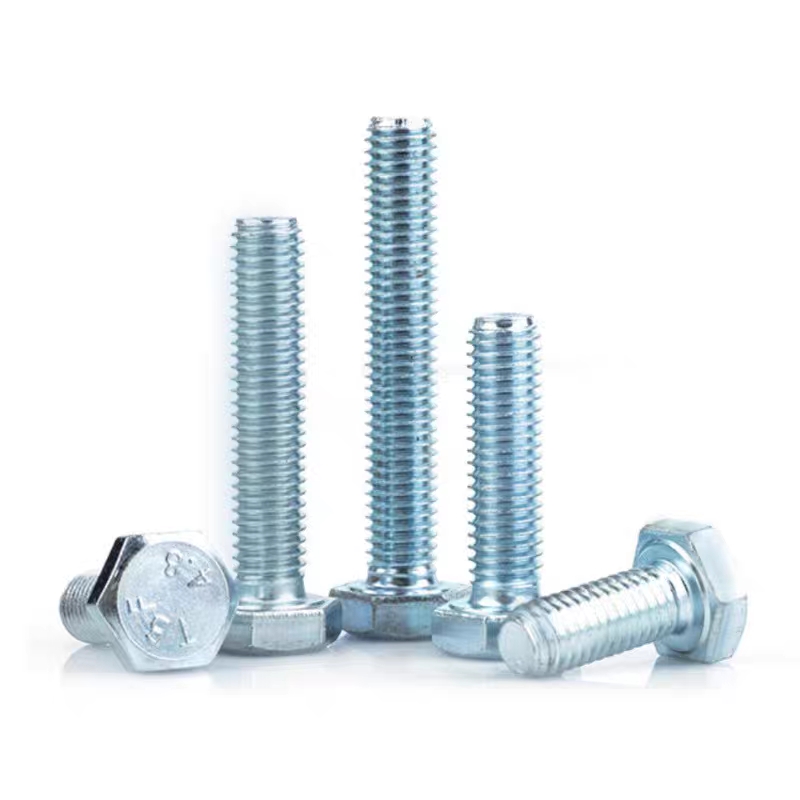
Electrogalvanized hinge bolts
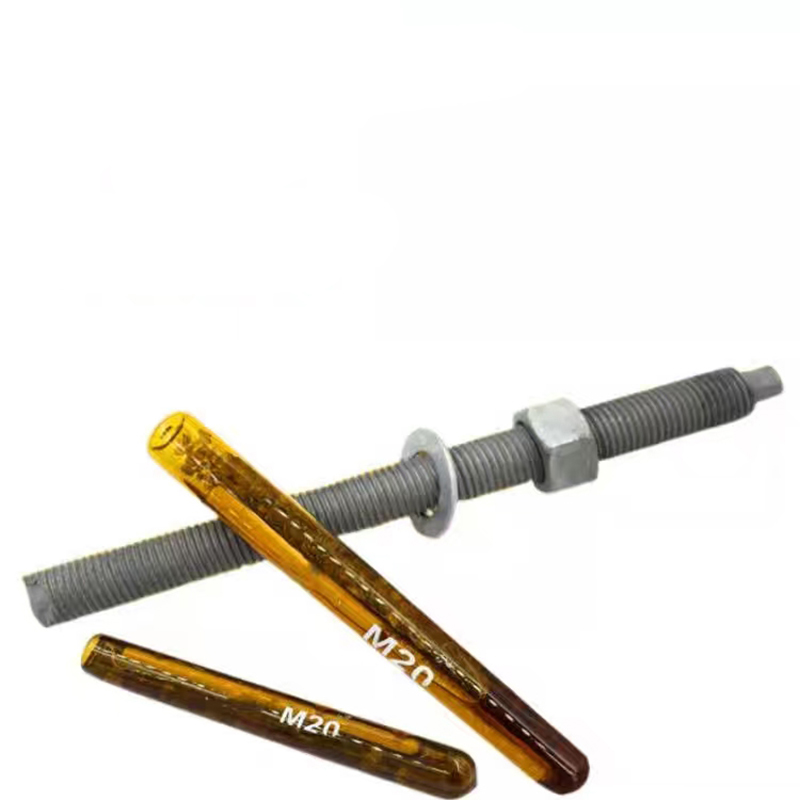
Swivel Bolt Series Structural Features • Basic Structure: Typically consists of a screw, a nut, and a central swivel joint. The screw has threads at both ends; one end connects to a fixed component, and the other end mates with the nut. The central swivel joint is usually spherical or cylindri...
Description
marker
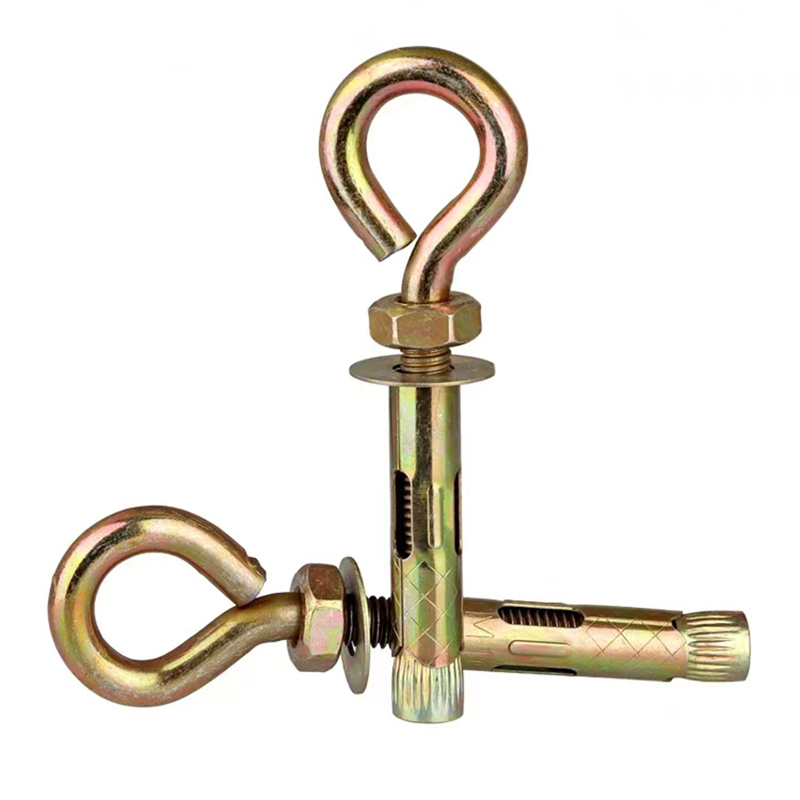
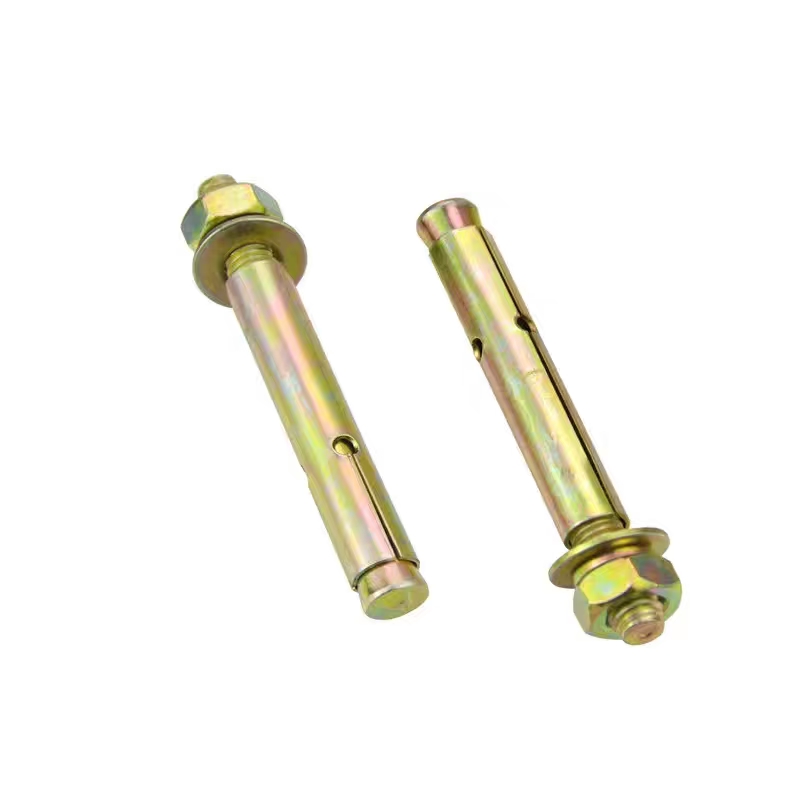
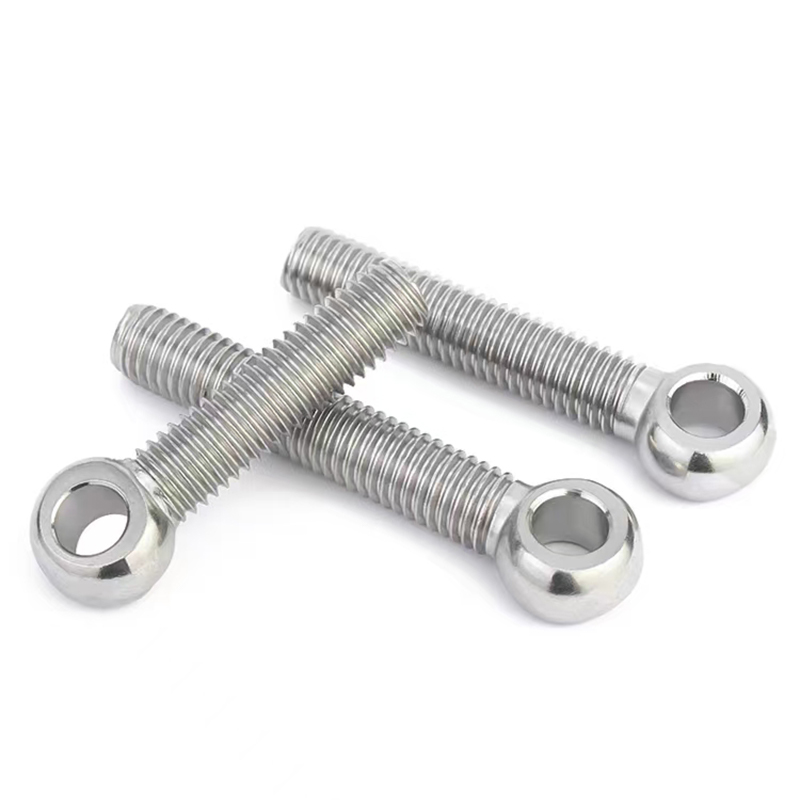
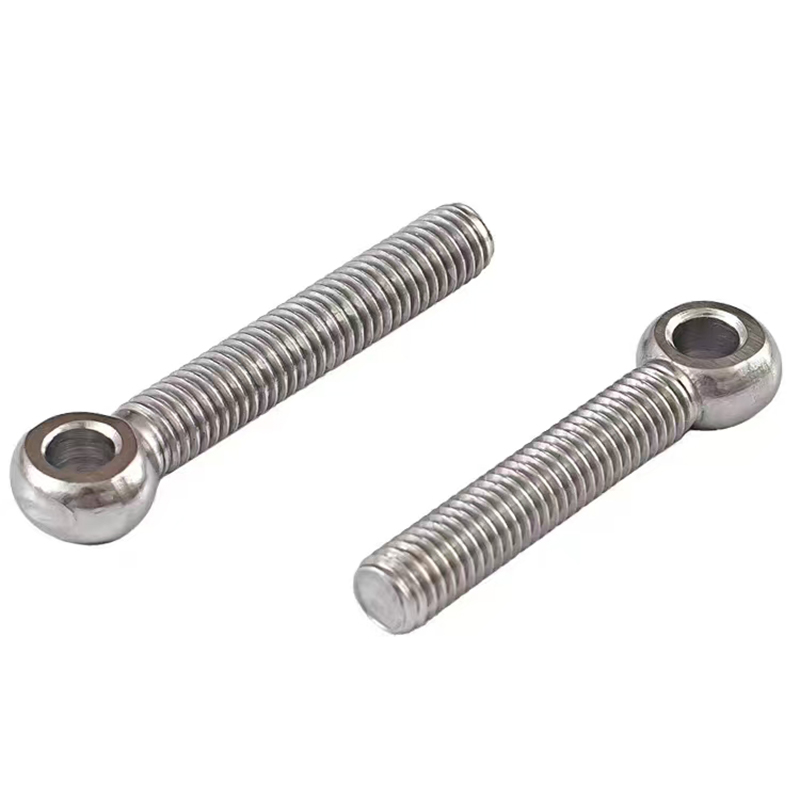
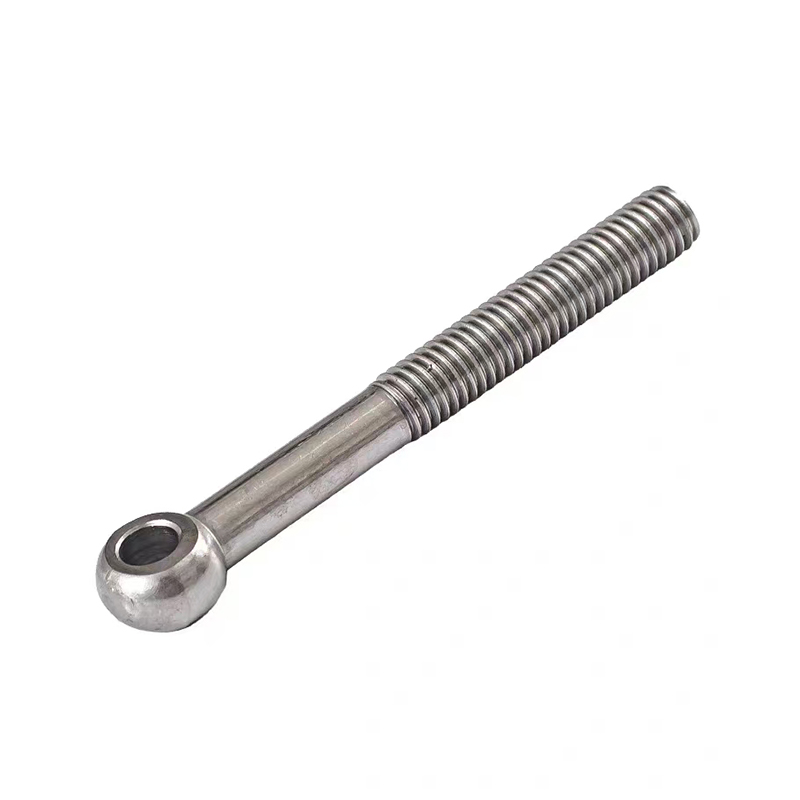
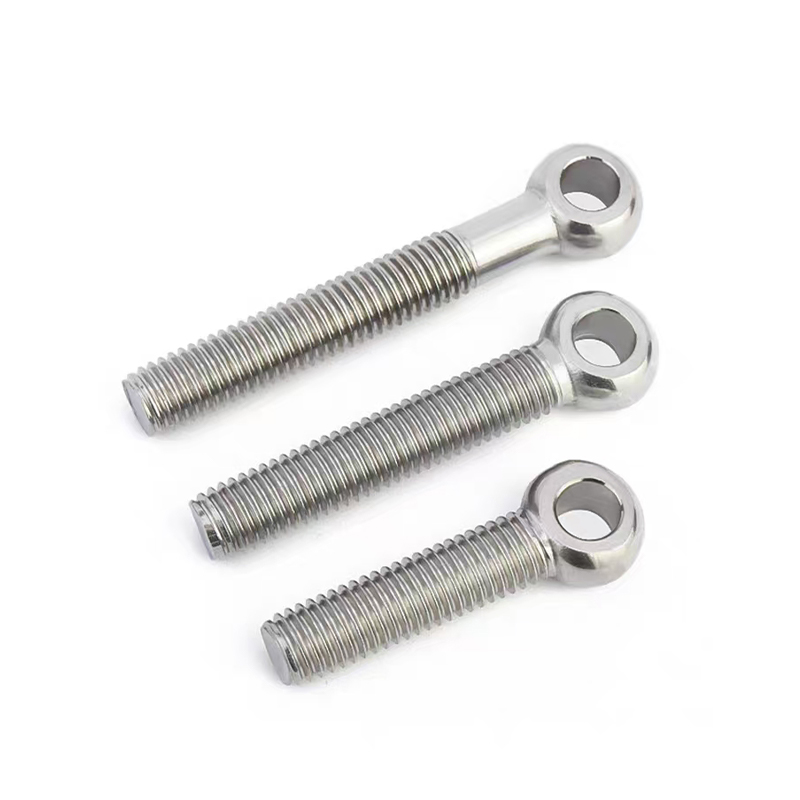
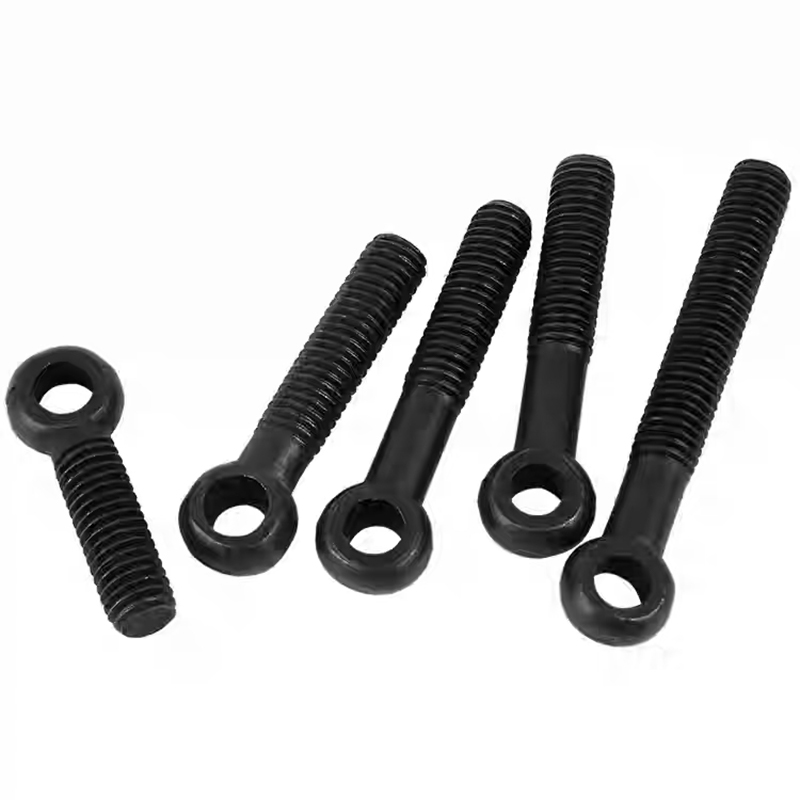
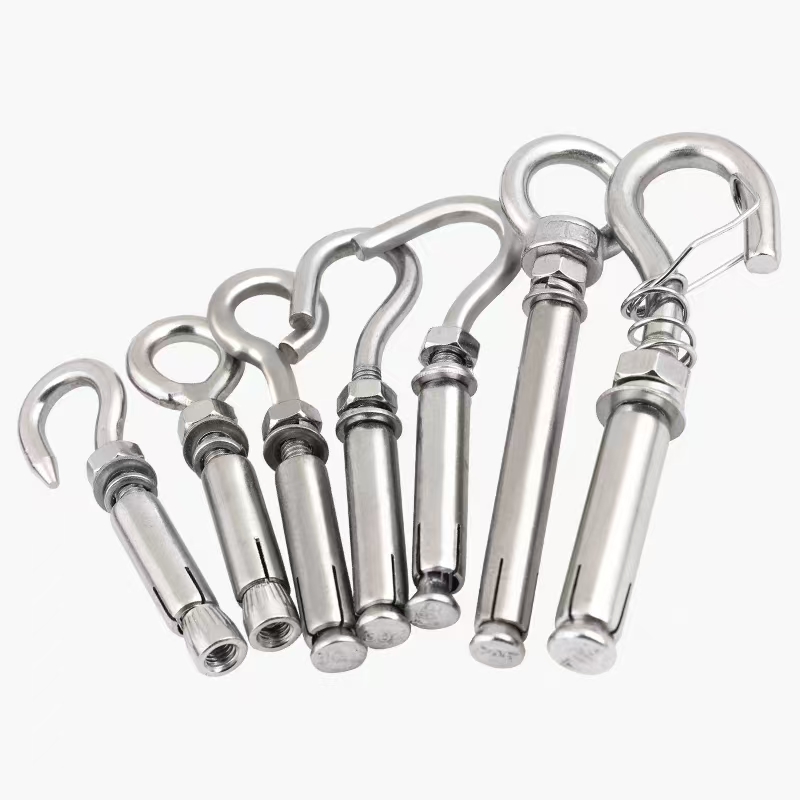
Swivel Bolt Series
Structural Features
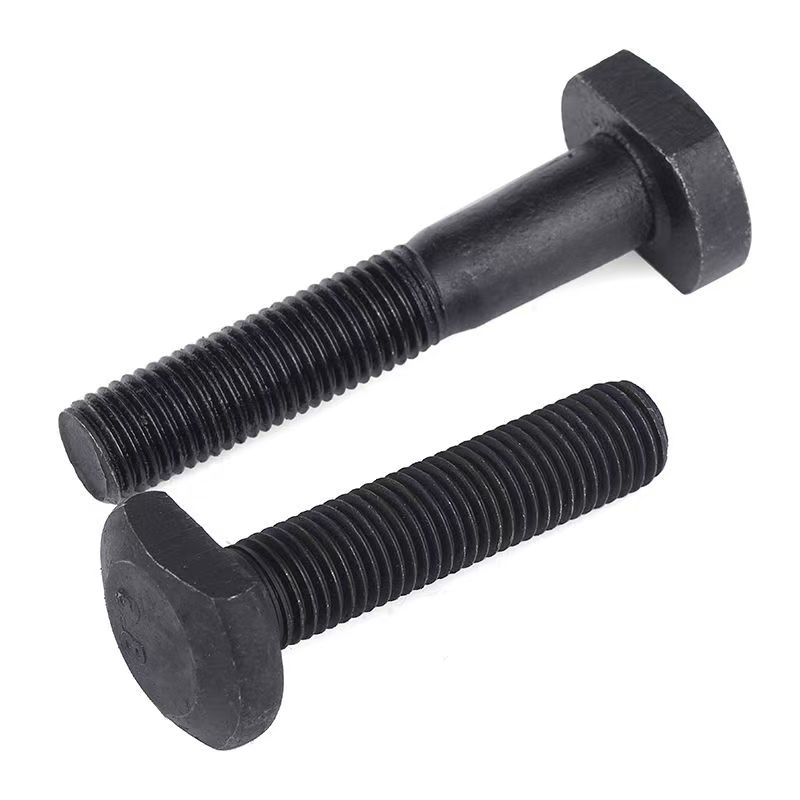
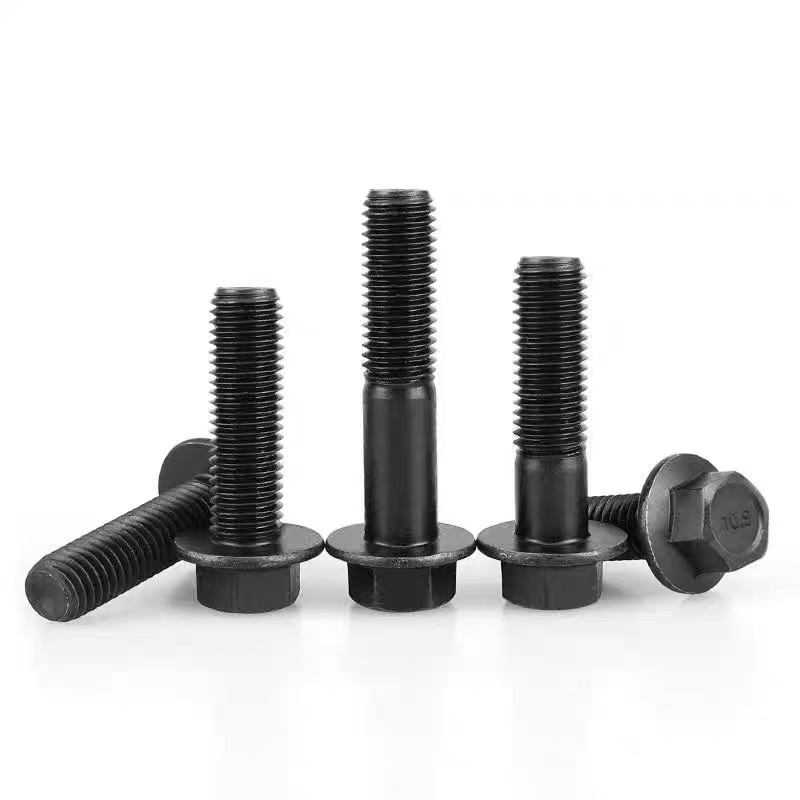
• Basic Structure: Typically consists of a screw, a nut, and a central swivel joint. The screw has threads at both ends; one end connects to a fixed component, and the other end mates with the nut. The central swivel joint is usually spherical or cylindrical, allowing for a certain degree of swinging and rotation.
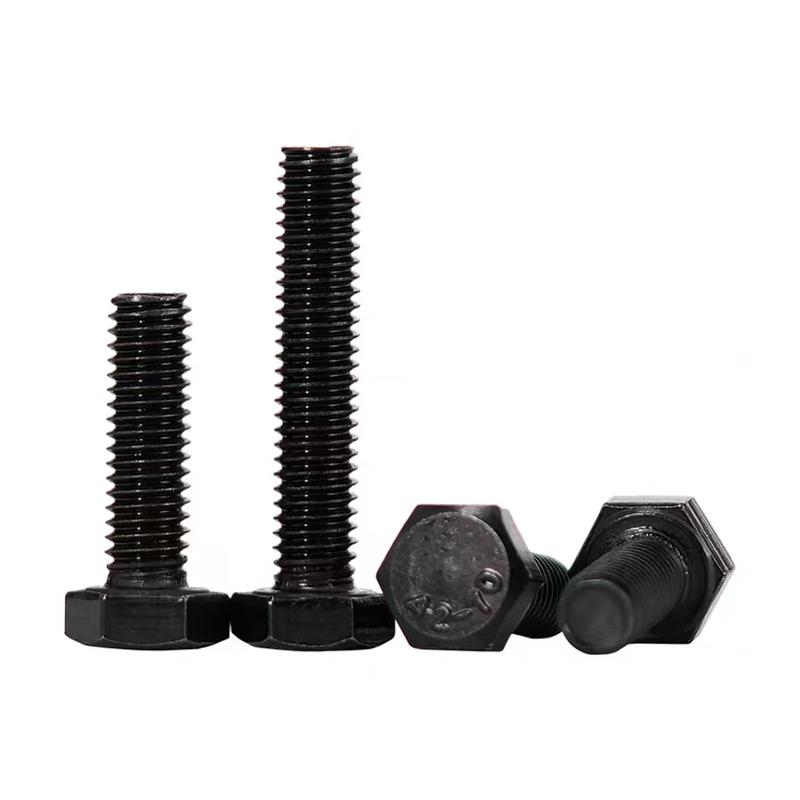
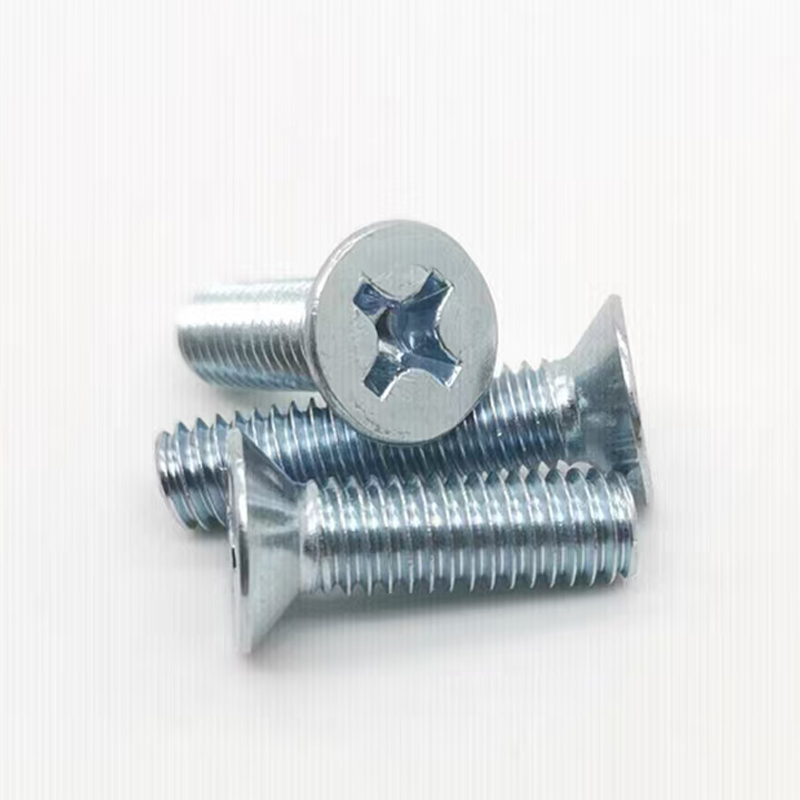
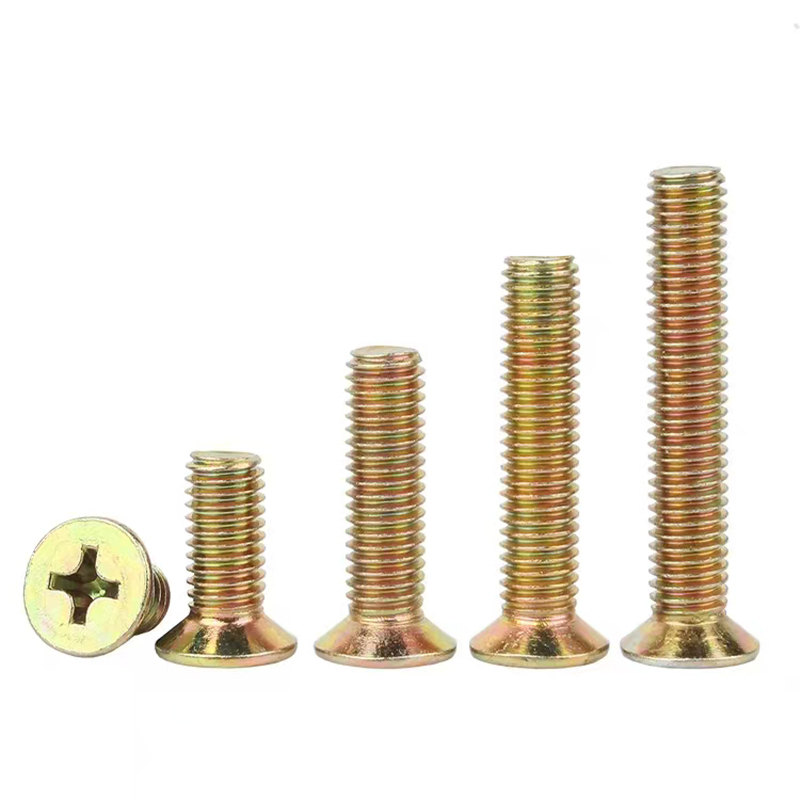
• Head Types: Diverse, common types include hexagonal head, round head, square head, countersunk head, and semi-countersunk head. Different head types are suitable for different installation scenarios and usage requirements.
Materials and Surface Treatment
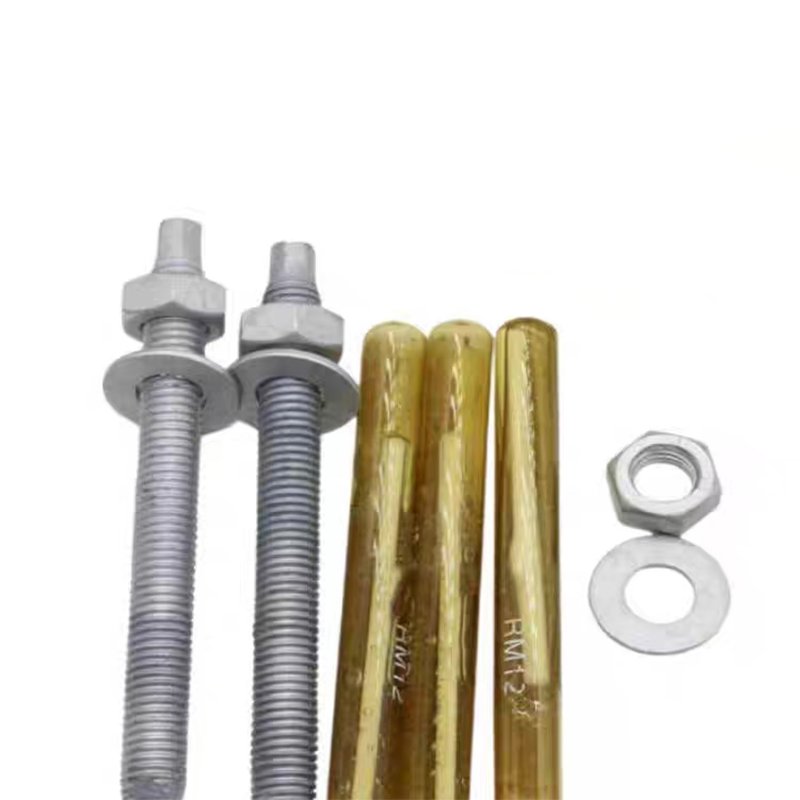
• Materials: Common materials include Q235, 45#, 40Cr, 35CrMoA, stainless steel 304, and stainless steel 316.
• Surface Treatment: Anti-corrosion measures include hot-dip galvanizing, diffusion coating, white plating, and color plating. High-strength bolts typically have a black oxide finish.
Specifications and Dimensions
Thread specifications generally range from M5 to M39. Different industries can select appropriate specifications according to actual needs. For example, the construction industry commonly uses M12-M24 specifications for steel structure connections, while the mechanical manufacturing field commonly uses M5-M10 specifications for connecting small mechanical equipment parts.
Working Principle
Through the movable characteristics of the swivel joint, the two connected components are allowed to move relative to each other within a certain range, such as swinging and rotation, effectively compensating for relative displacement and angular deviation between the components. At the same time, the threaded connection between the screw and the nut provides the fastening function, and the tightening degree of the nut can be adjusted as needed to achieve the appropriate connection strength.
Application Areas
• Mechanical Manufacturing: Commonly used in various mechanical transmission devices, automated production line equipment, etc., such as connections in chain drives and fixing of swinging mechanisms.
• Pipe Connections: Used to connect pipes of different diameters or with angular changes, as well as connections between pipes and valves, pumps, and other equipment, accommodating thermal expansion and contraction and vibration of the pipes.
• Automotive Manufacturing: Used in the suspension system, steering mechanism, engine mounts, and other parts of automobiles, ensuring the connection requirements of automotive components during movement.
• Building and Decoration: Plays a role in building curtain walls, door and window installation, and movable furniture, such as connection nodes of curtain walls and connection parts of movable furniture.
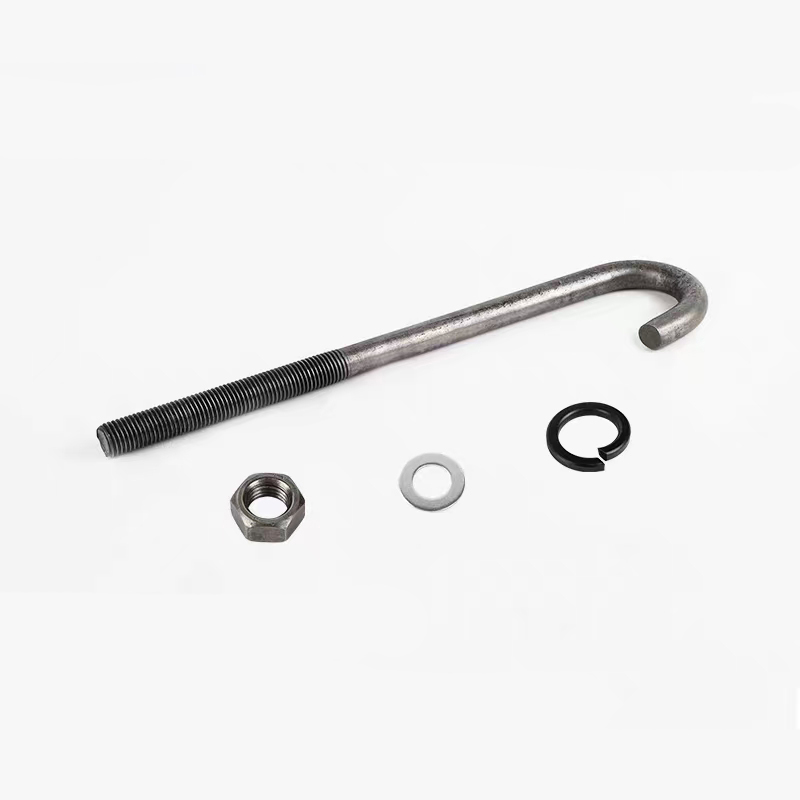
Marking Example
Taking a hinge bolt with thread specification d=M10, nominal length l=100mm, performance grade 4.6, and without surface treatment as an example, its marking is: Bolt GB 798 M10×100.