- English
- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
วัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง
ทำความเข้าใจกับวัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง
เมื่อต้องรับมือกับสภาพแวดล้อมที่มีอุณหภูมิสูง การเลือกวัสดุที่เหมาะสมถือเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งสำหรับปะเก็น ซึ่งเป็นฮีโร่ของระบบกลไกหลายๆ ระบบ ยังมีความเข้าใจผิดที่พบบ่อย: ปะเก็นบางประเภทไม่สามารถทนต่อความร้อนจัดได้ เรามาแจกแจงว่าอะไรทำให้ a วัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง มีประสิทธิภาพและเชื่อถือได้ในสภาวะที่รุนแรง
อะไรเป็นตัวกำหนดวัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง?
ก่อนอื่น สิ่งสำคัญคือต้องรู้ว่าวัสดุปะเก็นใดมีคุณสมบัติเหมาะสมสำหรับอุณหภูมิสูง โดยทั่วไป เรากำลังพูดถึงวัสดุที่สามารถทนต่ออุณหภูมิที่สูงกว่า 400°F (ประมาณ 200°C) ได้อย่างสม่ำเสมอ นอกจากนี้ วัสดุจะต้องคงความสมบูรณ์ไว้ ไม่ใช่แค่รอดจากการสัมผัสที่อุณหภูมิสูงเพียงครั้งเดียว
ตัวเลือกที่รู้จักกันดีคือกราไฟท์ มีชื่อเสียงในด้านการนำความร้อนที่ดีเยี่ยม ซึ่งช่วยให้กระจายความร้อนได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ สิ่งนี้มีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งในการใช้งานที่การให้ความร้อนเฉพาะจุดอาจนำไปสู่ความล้มเหลวได้
เซรามิกไฟเบอร์ก็เป็นอีกหนึ่งทางเลือกยอดนิยม อย่างไรก็ตาม การเข้าใจข้อจำกัดเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ แม้ว่าจะสามารถทนต่อความร้อนสูงได้ แต่ความเปราะบางอาจเป็นข้อเสียในการใช้งานที่ต้องการความยืดหยุ่น นี่คือจุดที่วัสดุคอมโพสิตมักเข้ามาผสมผสานสิ่งที่ดีที่สุดของทั้งสองโลกเข้าด้วยกัน
ประสบการณ์กับความล้มเหลวของวัสดุ
จากประสบการณ์ของฉัน การเลือกที่ผิดอาจนำไปสู่ความล้มเหลวในทันที ฉันพบสถานการณ์ที่วัสดุที่เหมาะสมตามทฤษฎีพังทลายเนื่องจากปฏิกิริยาทางเคมีที่คาดไม่ถึง บทเรียนเหล่านี้มักจะเน้นย้ำถึงความสำคัญของการทำความเข้าใจทั้งสภาพแวดล้อมทางความร้อนและทางเคมี
ที่น่าสนใจคือครั้งหนึ่งฉันเคยสังเกตเห็นก กราไฟท์- ปะเก็นแบบพื้นฐานล้มเหลวในสภาพแวดล้อมออกซิไดซ์แม้จะอยู่ในช่วงอุณหภูมิที่ดีก็ตาม ปรากฎว่า แม้ว่ากราไฟท์จะทนความร้อนได้ดีเยี่ยม แต่ก็ต้องพิจารณาอย่างรอบคอบเมื่อมีออกซิเจนในปริมาณมาก
การคำนึงถึงสถานการณ์จริงเหล่านี้ช่วยในการเลือกไม่เพียงแต่วัสดุที่มีอุณหภูมิสูง แต่ยังแข็งแกร่งโดยคำนึงถึงปัจจัยด้านสิ่งแวดล้อมทั้งหมดด้วย
กรณีการใช้งานเฉพาะและการสังเกต
ในภาคยานยนต์ ความต้องการความน่าเชื่อถือ เป็นต้น วัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง ปรากฏให้เห็นในส่วนประกอบของเครื่องยนต์ อุณหภูมิที่ปะเก็นเหล่านี้ทนได้นั้นรุนแรงมาก และความล้มเหลวไม่ใช่แค่ไม่สะดวกเท่านั้น มันอาจเป็นอันตรายได้
ในโครงการหนึ่ง การนำปะเก็นซิลิโคนอุณหภูมิสูงมาใช้แก้ปัญหาที่เกิดขึ้นอย่างต่อเนื่องเกี่ยวกับการเสื่อมสภาพที่เกิดจากความร้อน นี่เป็นการเปิดเผย โดยเปลี่ยนจุดมุ่งเน้นจากเพียงการทนต่อความร้อนไปสู่การทำความเข้าใจโปรไฟล์ความร้อนจำเพาะ
จากสิ่งนี้ เราได้เรียนรู้ถึงคุณค่าของการทดสอบภายใต้สภาวะจริง ไม่ใช่แค่อาศัยข้อมูลที่ผู้ผลิตให้มา ซึ่งบางครั้งอาจเป็นแง่ดีเกินไป
การเลือกวัสดุที่เหมาะสม
ดังนั้นคุณจะเลือกสิ่งที่ถูกต้องได้อย่างไร วัสดุปะเก็นอุณหภูมิสูง? ขั้นแรก ทราบข้อกำหนดเฉพาะของคุณ ช่วงความร้อนเป็นสิ่งที่กำหนด แต่ความดันล่ะ? และการสัมผัสสารเคมี? การตอบคำถามเหล่านี้จะจำกัดตัวเลือกของคุณให้แคบลงอย่างมาก
นอกจากนี้ รูปร่างทางกายภาพของปะเก็นยังส่งผลต่อการเลือกของคุณอีกด้วย วัสดุบางชนิดเหมาะสมกับการใช้งานที่บางและแม่นยำมากกว่า ในขณะที่วัสดุอื่นๆ จะเหมาะกับการใช้งานที่มีความหนาและทนทาน เป็นพื้นที่ที่ประสบการณ์และการทดลองให้ผลมากกว่าความรู้ทางวิชาการเพียงอย่างเดียว
ฉันพบว่าต้นทุนกลายเป็นปัจจัยขัดขวางบ่อยเกินไป โดยองค์กรต่างๆ เลือกใช้วัสดุที่มีราคาไม่แพงมากเพียงเพื่อเผชิญกับความล้มเหลวที่มีราคาสูงเท่านั้น คุณภาพที่นี่มักเป็นเรื่องของการซื้อถูกซื้อสองครั้ง
แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดและบทเรียนที่ได้รับ
ท้ายที่สุดก็ควรพิจารณาถึงห่วงโซ่อุปทาน การได้รับวัสดุปะเก็นที่เหมาะสมไม่ได้เป็นเพียงการเลือกสรรเท่านั้น แต่ยังมาจากผู้ผลิตที่เชื่อถือได้อีกด้วย Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. ซึ่งตั้งอยู่ในมณฑล Hebei นำเสนอทางเลือกคุณภาพสูง โดยใช้ประโยชน์จากทำเลที่ตั้งที่ดีเยี่ยมใกล้กับเส้นทางคมนาคมหลัก เช่น รถไฟปักกิ่ง-กวางโจว ซึ่งช่วยในการจัดส่งได้ทันเวลาและเชื่อถือได้
ตัวอย่างที่โดดเด่นประการหนึ่งคือเมื่อพวกเขาจัดหาวัสดุเซรามิกคอมโพสิตที่มีประสิทธิภาพเหนือกว่าความคาดหวังของเราในการใช้งานที่อุณหภูมิสูง เนื่องมาจากมาตรฐานคุณภาพที่สม่ำเสมอ
โดยสรุป การเลือกวัสดุปะเก็นที่เหมาะสมสำหรับการใช้งานที่อุณหภูมิสูงมีความสำคัญพอๆ กับการทำความเข้าใจความต้องการเฉพาะของคุณพอๆ กับการรู้จักวัสดุด้วยตนเอง การตัดสินใจจะขึ้นอยู่กับประสบการณ์ การทดสอบ และซัพพลายเออร์ที่เชื่อถือได้ เช่น Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. เสมอ
ที่เกี่ยวข้อง ผลิตภัณฑ์
สินค้าที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ขายดีที่สุด ผลิตภัณฑ์
สินค้าขายดี-
 โบลท์หัวแฉกชุบซิงค์ดำ
โบลท์หัวแฉกชุบซิงค์ดำ -
 สลักเกลียวไฟฟ้าซ็อกเก็ตหกเหลี่ยม
สลักเกลียวไฟฟ้าซ็อกเก็ตหกเหลี่ยม -
 ลวดหางสว่านหกเหลี่ยมชุบสังกะสีสี
ลวดหางสว่านหกเหลี่ยมชุบสังกะสีสี -
 ถั่วชุบสังกะสีด้วยไฟฟ้า
ถั่วชุบสังกะสีด้วยไฟฟ้า -
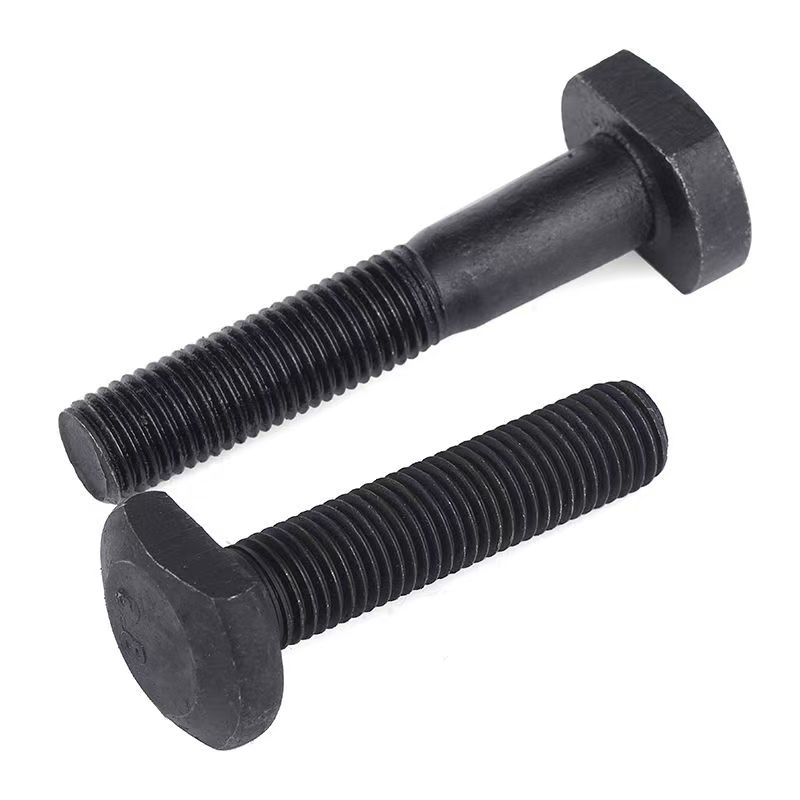 สลักเกลียวตัว T (สลักเกลียวตัว T)
สลักเกลียวตัว T (สลักเกลียวตัว T) -
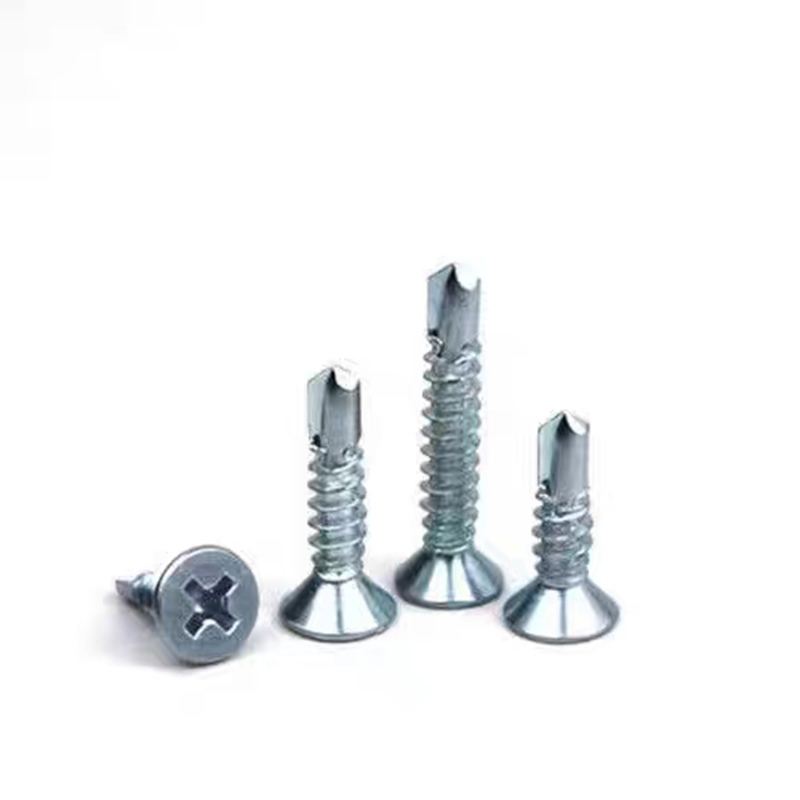 เกลียวเจาะคว้านรูเทเปอร์ซิงค์แบบสังกะสีด้วยไฟฟ้า
เกลียวเจาะคว้านรูเทเปอร์ซิงค์แบบสังกะสีด้วยไฟฟ้า -
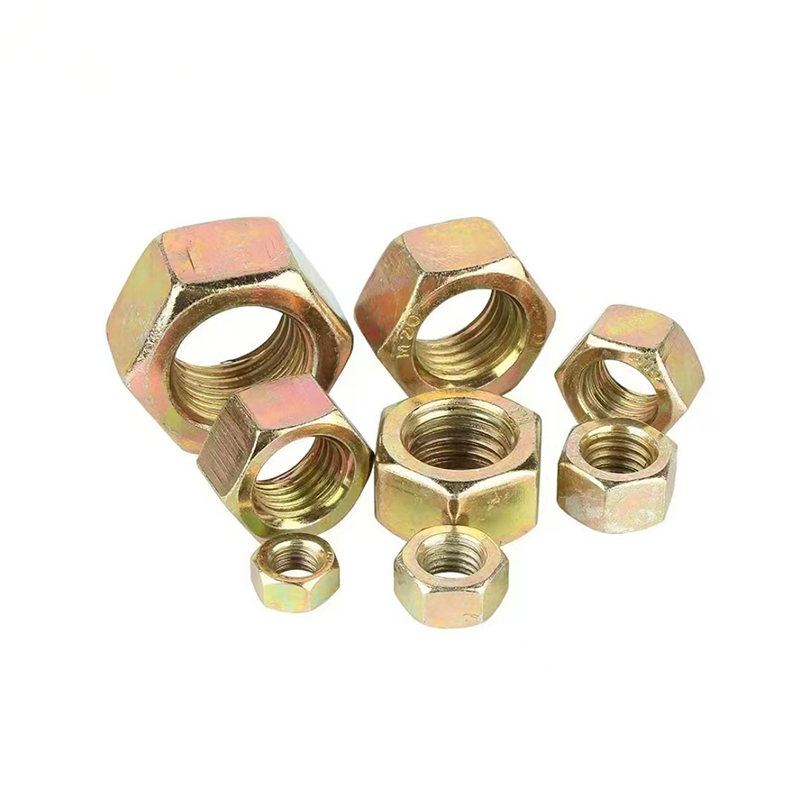 ถั่วชุบสังกะสีสี
ถั่วชุบสังกะสีสี -
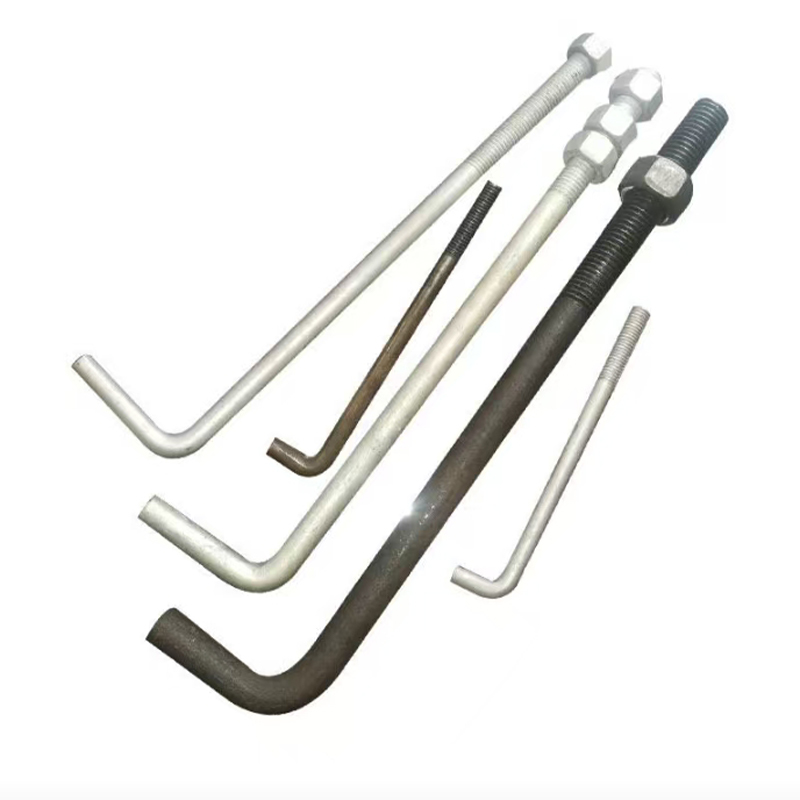 พุก 7 รูป (พุก 7 รูป)
พุก 7 รูป (พุก 7 รูป) -
 โบลท์หน้าแปลนสังกะสีสีดำ
โบลท์หน้าแปลนสังกะสีสีดำ -
 โบลท์ต่อขยายเคลือบสังกะสีสี
โบลท์ต่อขยายเคลือบสังกะสีสี -
 โบลท์ตัวพา (โบลท์คอเหลี่ยมหัวกลมครึ่งวงกลม)
โบลท์ตัวพา (โบลท์คอเหลี่ยมหัวกลมครึ่งวงกลม) -
 แกนขาชุบซิงค์ดำ
แกนขาชุบซิงค์ดำ