- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
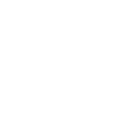
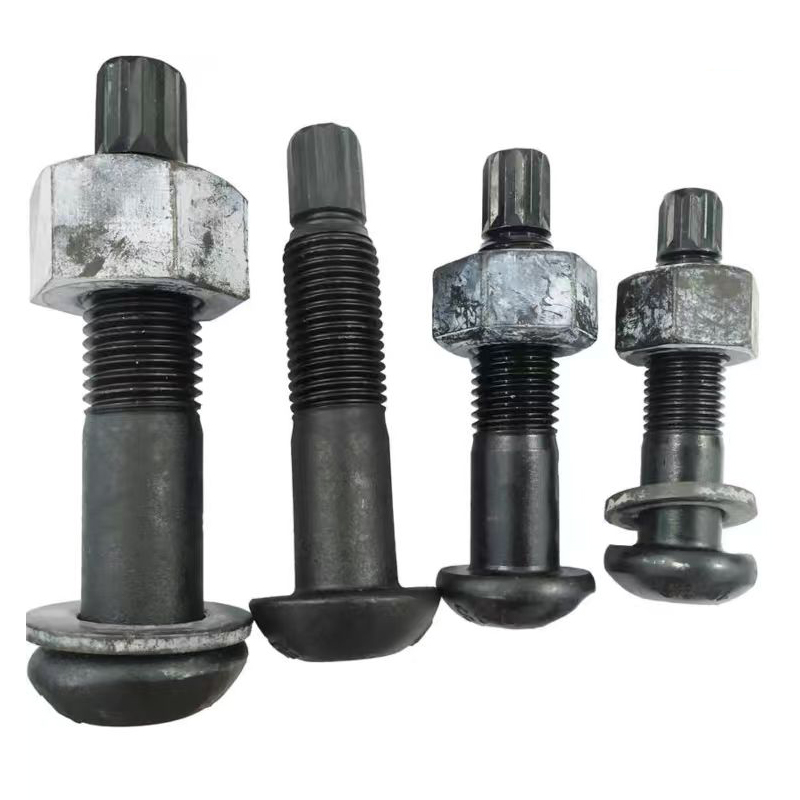
4 u bolt
Understanding 4 U Bolt Applications: A Practical Perspective
The term 4 U bolt might sound straightforward to those well-versed in hardware, but its applications and importance extend beyond simple fastening. As a crucial component in various engineering and construction projects, understanding its use can make a significant difference in project outcomes.
The Unknown Potential of U Bolts
At first glance, a 4 U bolt seems deceptively simple—a curved steel rod with threaded ends. It’s often taken for granted until you find yourself in a project where every bolt matters. The importance of choosing the correct size and material can't be overstated, as they influence the durability and strength of your entire assembly.
A common oversight is underestimating the significance of the bolt’s diameter and threading when securing heavy loads. In practice, a slightly undersized bolt can lead to catastrophic failures, proving that precision matters as much in bolts as in any other component.
Not to mention, the material quality from manufacturers like Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. plays a crucial role. Their website, zitaifasteners.com, showcases a range of products produced in China's largest fastener hub, ensuring reliability and accessibility.
Making the Right Choice
Decision-making regarding a 4 U bolt often revolves around application specifics. For instance, light-duty tasks might tolerate a lesser grade, whereas suspension bridges demand high-tensile materials. It’s the difference between using regular zinc-plated steel for a basic application and galvanizing it for high resistance to environmental wear.
When in doubt, factor in corrosion resistance. Bolts exposed to elements require protective coatings or inherently resistant materials like stainless steel. For those in the industry, this isn’t just advice—it's standard operating procedure.
Precision is key, especially when working with engineering specifications. A misjudgment in bolt size or material can halt progress, causing delays and often financial losses.
Handling Installation Issues
Installation can be its own hurdle. Improperly seated U bolts lead to uneven stress distribution. During my early days on site, I learned the hard way that torque specifications aren't merely guidelines—they are necessary for maintaining stability.
One lesson was understanding thread engagement. It’s not just about fitting a nut onto a bolt. Both should engage sufficiently to ensure a secure fit, ideally three threads or more beyond the nut.
Another is the alignment during installation. A crooked bolt not only looks unprofessional but could compromise the clamping force. Practically, consistent torque settings help prevent issues down the line.
Practical Applications Worth Noting
The scale of projects utilizing 4 U bolts varies. While they hold pipes and tubes in place universally across industries, each application might demand specific attention to load and application site conditions.
Consider trucks. Their suspension systems rely heavily on these bolts to secure leaf springs, where failure isn't an option. Thus, regular checks and maintenance constitute a non-negotiable routine.
Whether for marine applications or industrial mounts, these bolts quite literally keep our world together. Their design versatility allows them to adapt across multiple scenarios seamlessly.
Insights from Experienced Hands
Looking back at various projects, some successful and others less so, I've realized the real learning curve lies in understanding the operational nuances of seemingly simple components. Remember, the devil’s in the details.
I encourage using resources like those provided by Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. Their expertise, rooted in China’s bustling manufacturing district, offers insights into material science and engineering standards.
In essence, a 4 U bolt is more than a piece of metal—it’s a vital part of the engineering puzzle. Treat it as such, and it will serve your projects faithfully.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
 Colored zinc-plated gaskets
Colored zinc-plated gaskets -
 Hot-dip galvanized embedded plate
Hot-dip galvanized embedded plate -
 Colored zinc-plated nuts
Colored zinc-plated nuts -
 Stud bolts
Stud bolts -
 Basket bolts
Basket bolts -
 Hexagon socket hot-dip galvanized bolts
Hexagon socket hot-dip galvanized bolts -
 Electro-galvanized expansion hook
Electro-galvanized expansion hook -
 Steel structure welding studs
Steel structure welding studs -
 Electrogalvanized embedded plate
Electrogalvanized embedded plate -
 Hexagon socket electrogalvanized bolts
Hexagon socket electrogalvanized bolts -
 Electroplated galvanized gaskets
Electroplated galvanized gaskets -
 10.9S large hexagon bolts
10.9S large hexagon bolts