- Chinese
- French
- German
- Portuguese
- Spanish
- Russian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Arabic
- Irish
- Greek
- Turkish
- Italian
- Danish
- Romanian
- Indonesian
- Czech
- Afrikaans
- Swedish
- Polish
- Basque
- Catalan
- Esperanto
- Hindi
- Lao
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Cebuano
- Chichewa
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Dutch
- Estonian
- Filipino
- Finnish
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hmong
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Igbo
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembou..
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Burmese
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Pashto
- Persian
- Punjabi
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Samoan
- Scots Gaelic
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
- Kinyarwanda
- Tatar
- Oriya
- Turkmen
- Uyghur
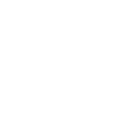
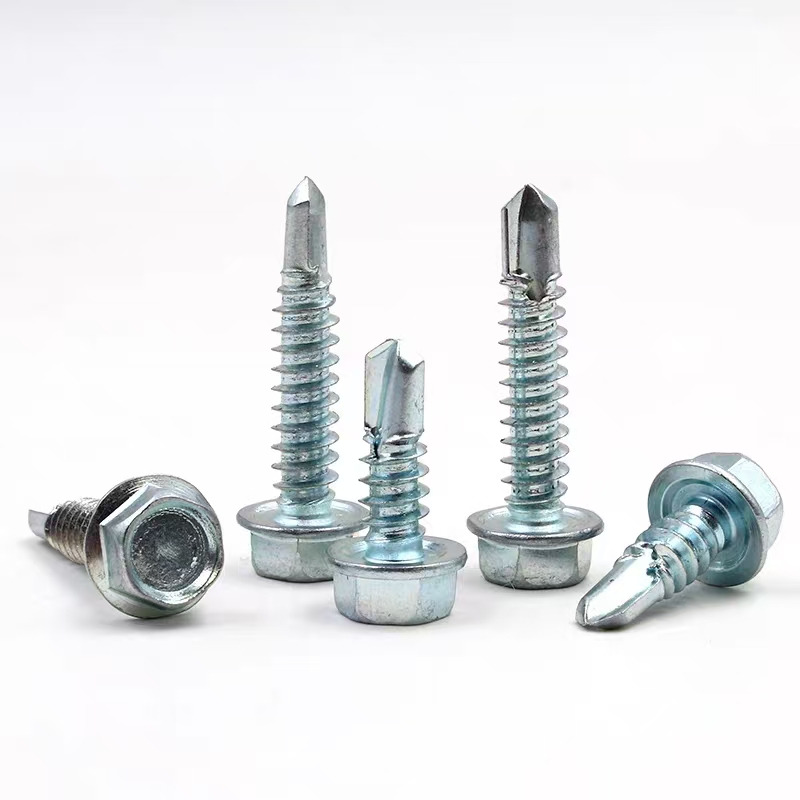
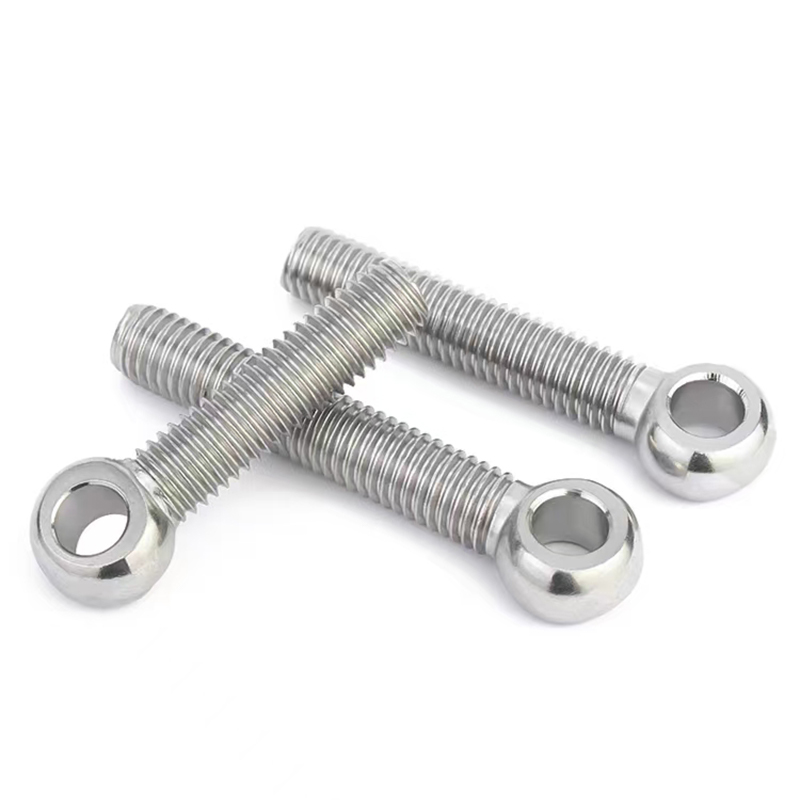
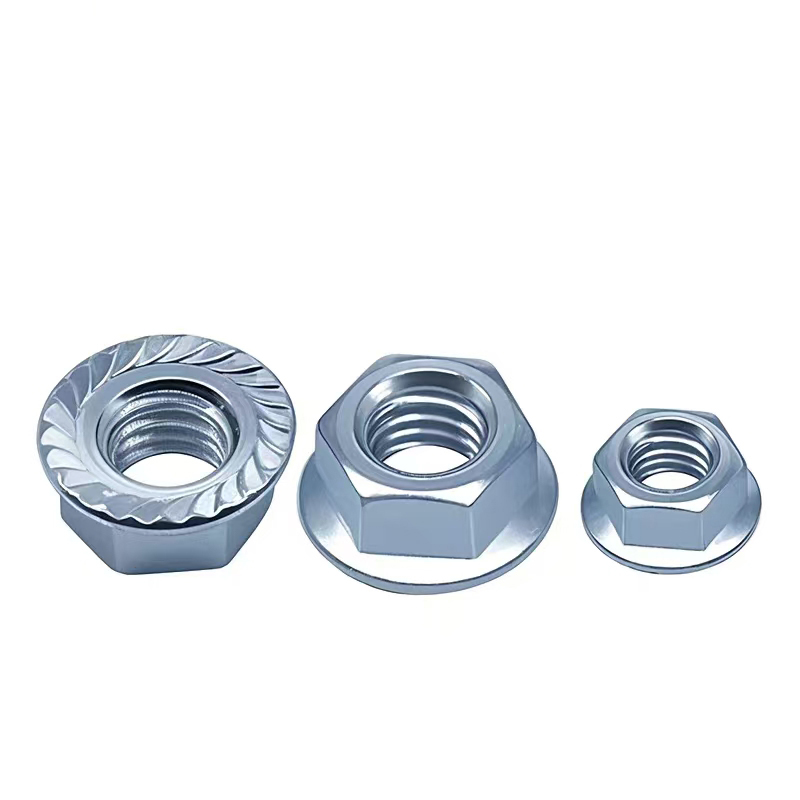
wholesale Embedded parts series
Understanding Wholesale Embedded Parts Series
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, the concept of wholesale Embedded parts series often gets misunderstood. Some see it merely as a bulk purchase opportunity; others think of it as a back-end component with little influence over the final product's quality. Yet, the reality is much more nuanced, demanding a blend of experience and instinct.
The Basics of Embedded Parts
When we talk about embedded parts, the term encompasses a range of components that are designed to be incorporated into larger systems. These could be anything from fasteners to connectors. What's critical here is the understanding that these components play a foundational role, despite often being hidden from view.
I remember a project where overlooking the quality of a simple embedded connector led to an entire batch failure. We had sourced parts from a new supplier, thinking it was just a cost-cutting measure. It turned out, we'd ignored vital quality standards, resulting in misalignment when integrated.
Every piece, no matter how insignificant it appears, contributes to the structural integrity and functionality of the final product. That's a hard-earned lesson many in the industry don't forget.
Wholesale Dynamics
What truly constitutes a 'wholesale' approach to embedded parts? It's not just bulk buying at discounted rates. At Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd., we've learned that strategic partnerships with suppliers can dramatically alter the dynamics. Our location in Hebei Province, near major transport routes, plays a part in leveraging these partnerships efficiently.
Take, for example, securing a consistent supply chain. When stocking up on fasteners, it's about guaranteeing consistency—both in delivery and part quality. We once faced a delay in a fastener shipment due to a misjudged storm in the Beijing-Guangzhou area. It was a stark reminder that logistics can make or break production schedules.
The key is aligning supply chain strategies with production schedules, ensuring no room for costly hiccups. Constant communication with suppliers is crucial in maintaining this balance.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance in embedded parts isn't just a checkbox exercise. It's a deeply involved process that includes meticulous testing at every stage. Our experience tells us that complacency here can lead to catastrophic failures at later stages.
Let me draw an example. Initial tests at a manufacturer's facility look promising, yet real-world challenges usually differ. This issue cropped up when testing under laboratory conditions failed to replicate the actual stresses on our parts during winter months.
Such instances reinforce the necessity of implementing rigorous, diverse testing procedures tailored to real-world environments, ensuring products withstand varied stresses.
The Role of Technology
With Industry 4.0 making waves, the integration of technology in managing embedded parts is indispensable. At Zitai Fasteners, we're seeing a shift towards digital solutions in inventory management systems. It’s more than just automation; it's about precision and foresight.
By integrating IoT solutions, we've achieved real-time monitoring of stock levels. This data-driven approach aids in preemptive ordering, eliminating bottlenecks and enhancing workflow efficiency.
The challenge, however, lies in the necessary investment and retraining processes, which can be a significant hurdle, particularly for smaller outfits. Many are still pondering the ROI, though evidence points towards long-term gains.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Looking forward, a notable trend is the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials in the manufacturing of embedded parts. This shift is both consumer and regulation-driven, compelling manufacturers to rethink their material sourcing strategies.
The market is also witnessing a rise in bespoke solutions, with an increasing preference for customized parts that cater to specific industry needs. Handan Zitai Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is exploring these avenues, integrating customer feedback to shape product designs and offerings.
Overall, success in the wholesale Embedded parts series domain hinges on adaptability, understanding the nuances of the supply chain, maintaining stringent quality controls, and embracing technology. It’s a comprehensive approach that transforms mere parts into critical components of innovation.
Related products
Related products
Best selling products
Best selling products-
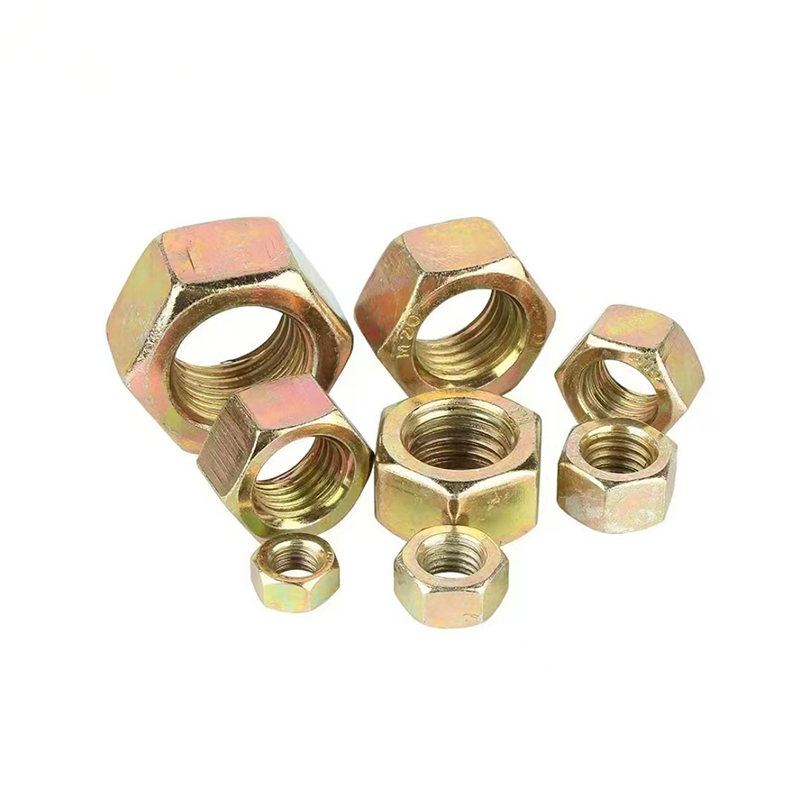 Colored zinc-plated nuts
Colored zinc-plated nuts -
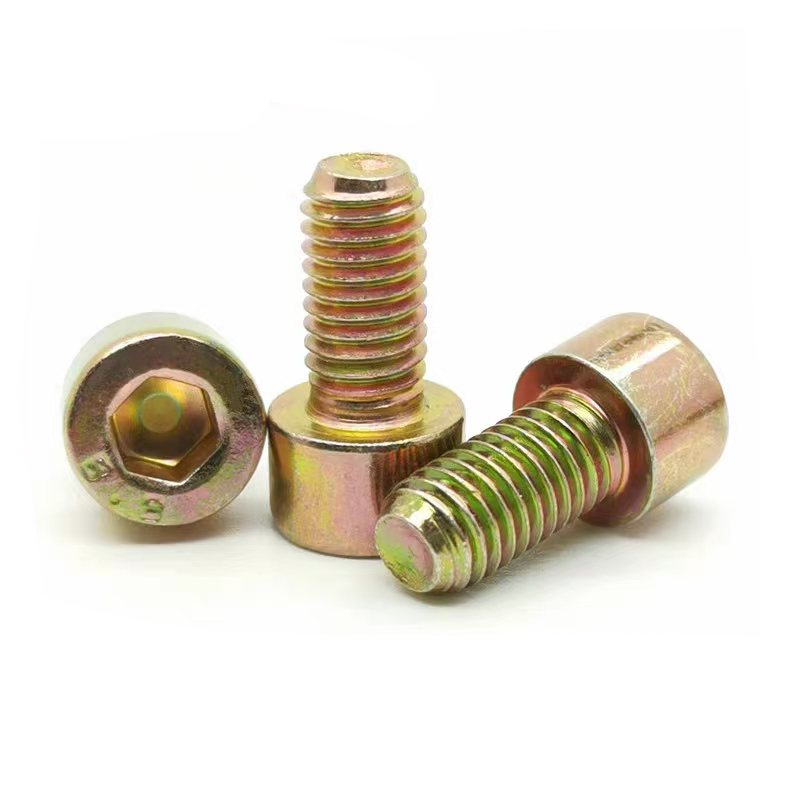 Hexagon socket colored zinc-plated bolts
Hexagon socket colored zinc-plated bolts -
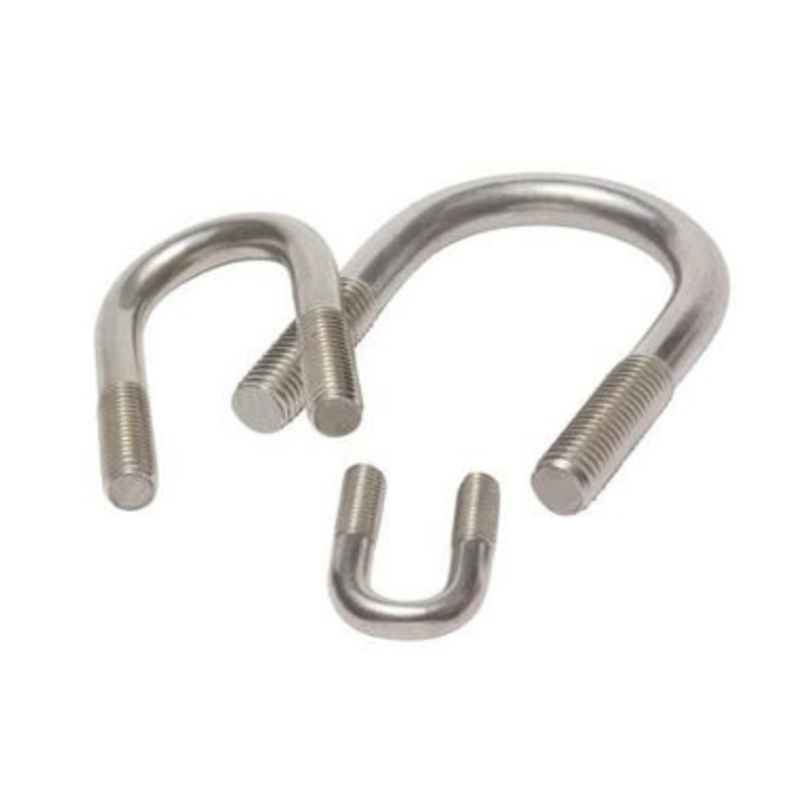 U-bolts
U-bolts -
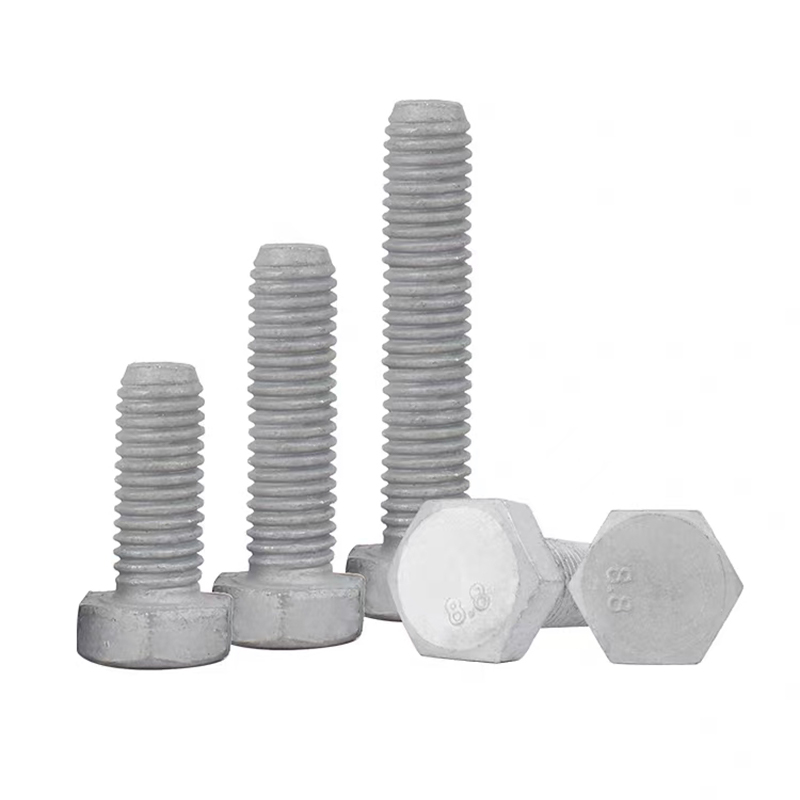
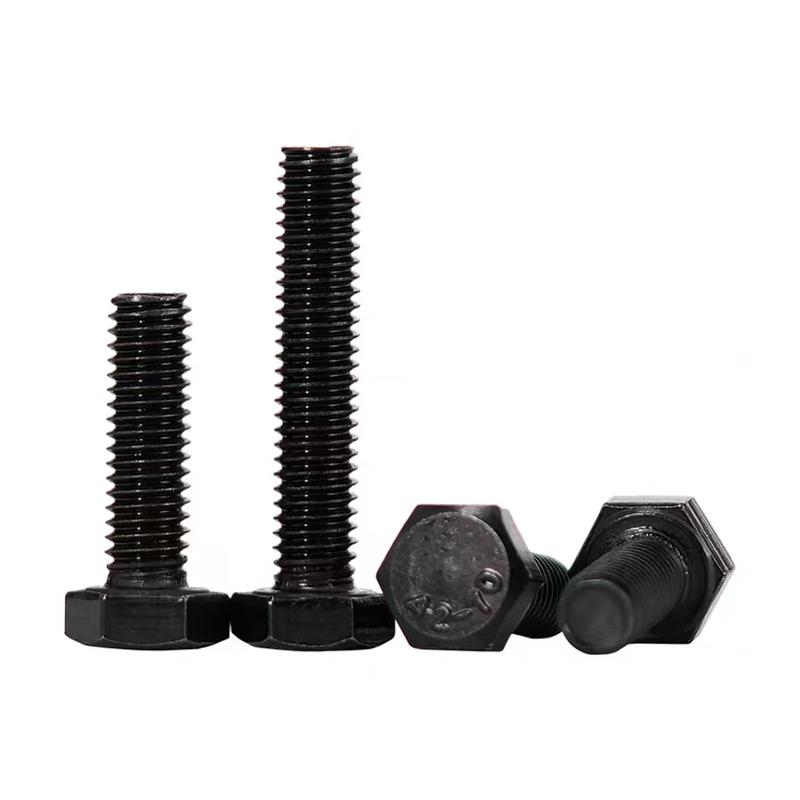 Black zinc plated hexagonal bolts
Black zinc plated hexagonal bolts -
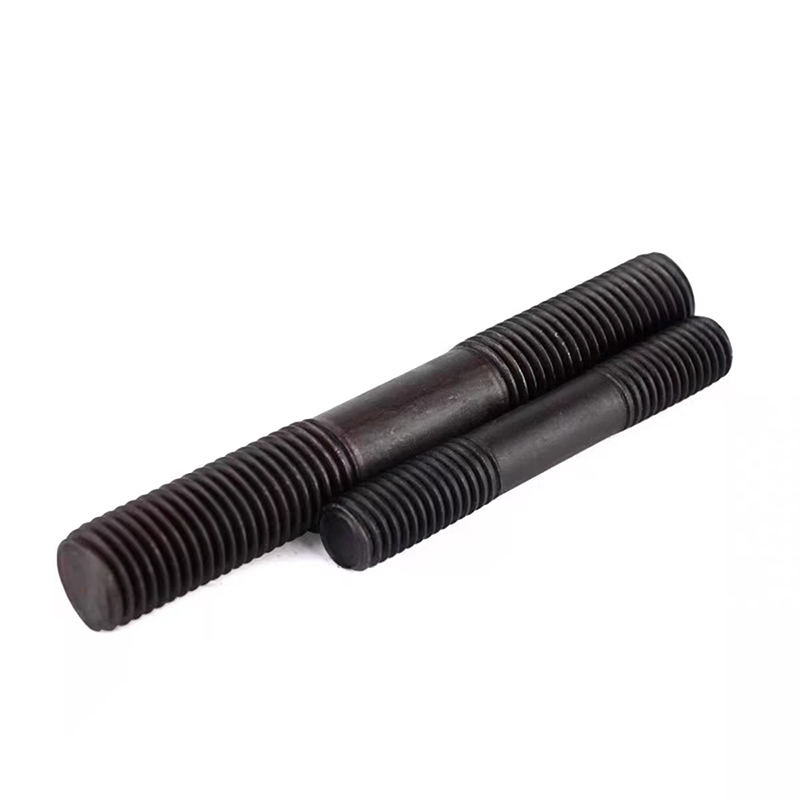
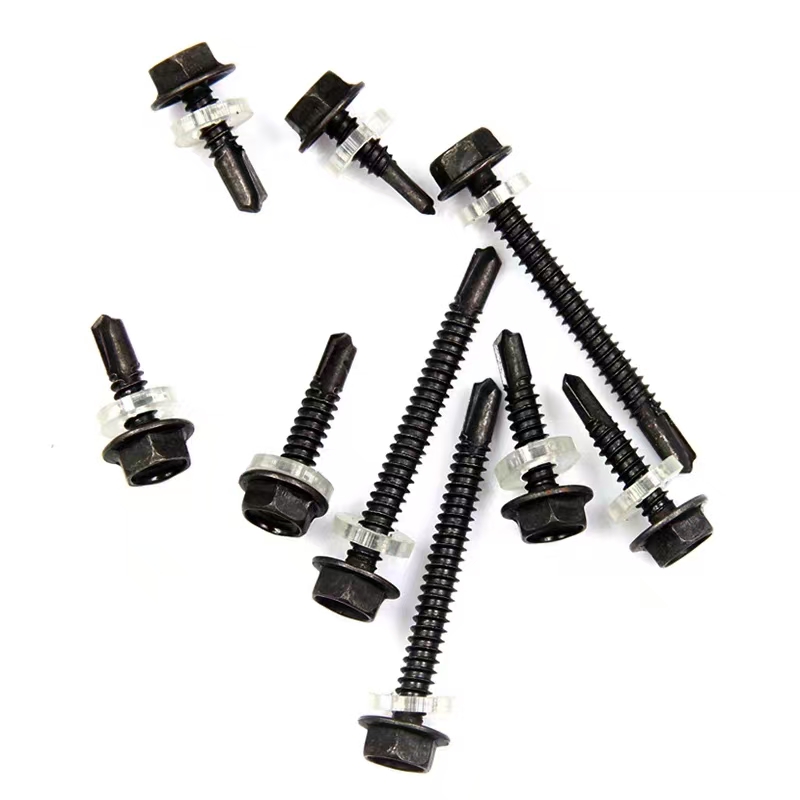 Black zinc-plated hexagonal drill tail wire
Black zinc-plated hexagonal drill tail wire -
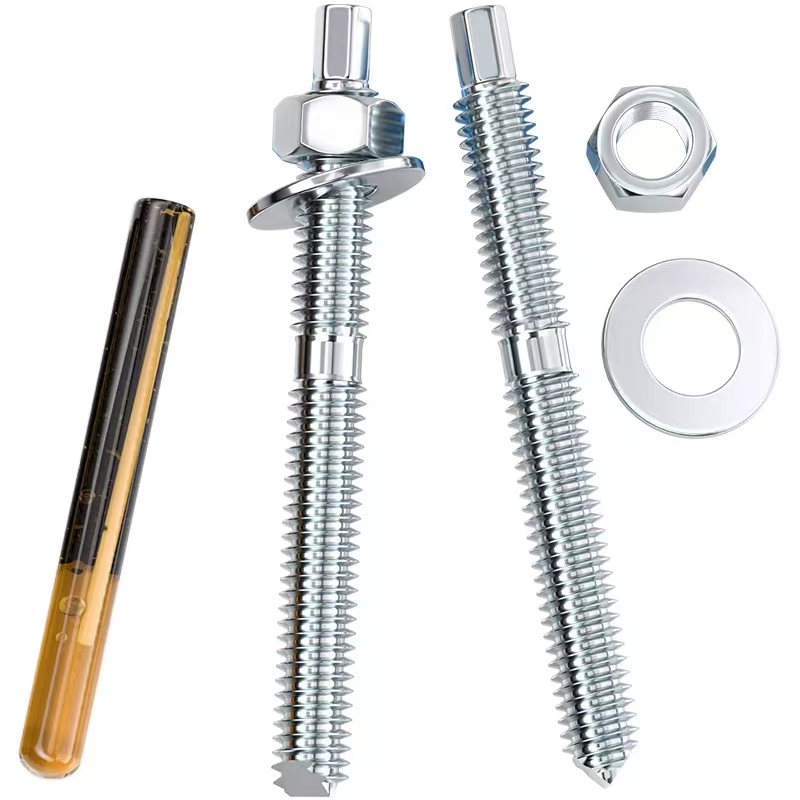 Electrogalvanized chemical bolts
Electrogalvanized chemical bolts -
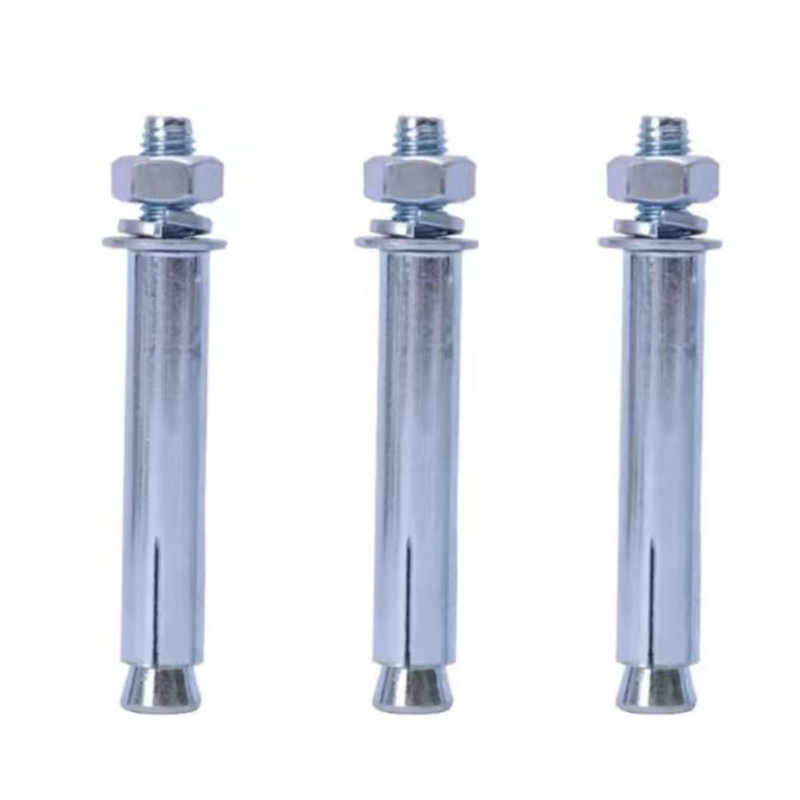 Electrogalvanized expansion bolts
Electrogalvanized expansion bolts -
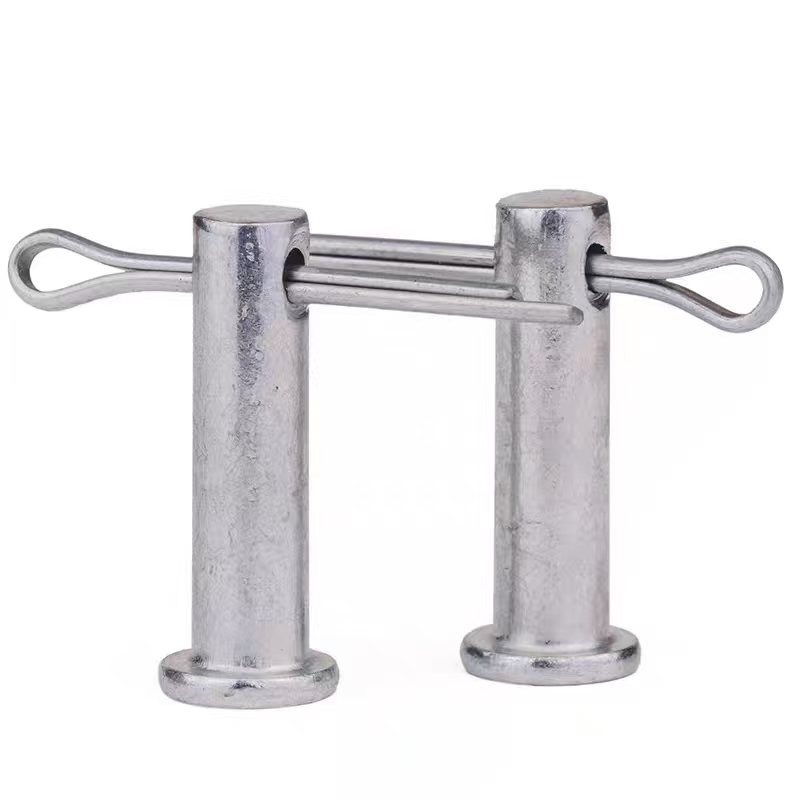
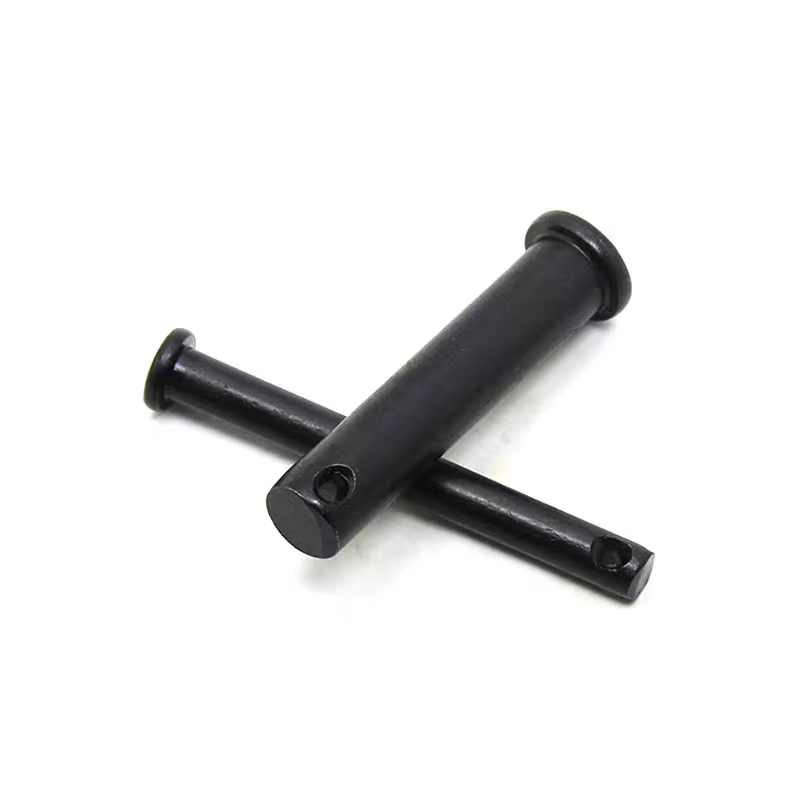 Black zinc plated pin shaft
Black zinc plated pin shaft -
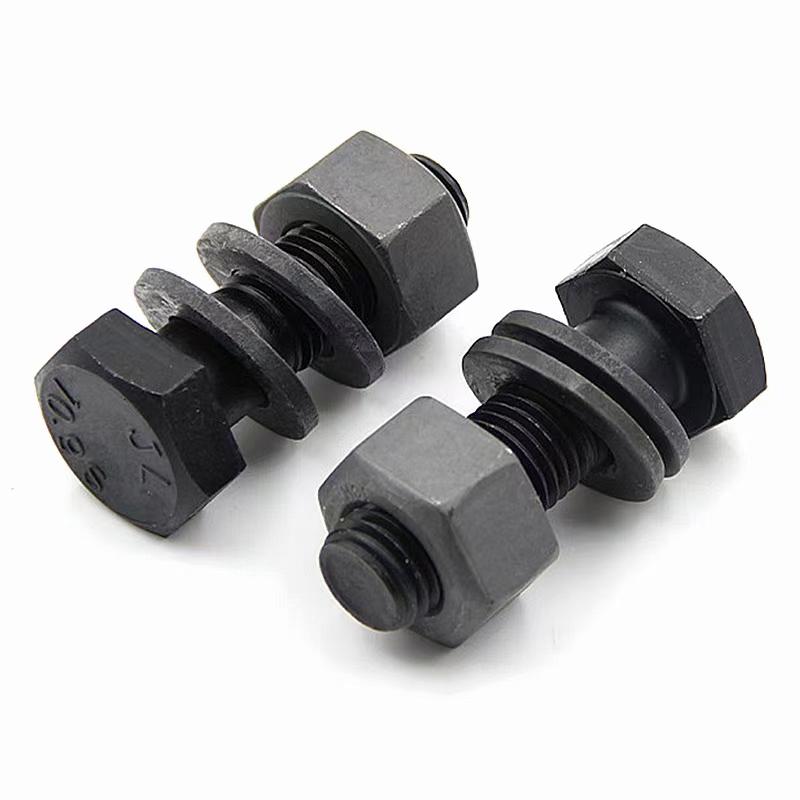
 10.9S Torsion Shear Bolts
10.9S Torsion Shear Bolts -
 Black zinc plated countersunk cross bolts
Black zinc plated countersunk cross bolts -
 Black zinc flange bolts
Black zinc flange bolts -
 Hexagon socket electrogalvanized bolts
Hexagon socket electrogalvanized bolts